Publication reference
Title: The Asset & Maintenace Management Lemnicate
Author: Jan Stoker
Publisher: SSAMM (Click Here)
Publication platform: SSAMM Academy – ssammeducation.com
ISBN/EAN: 978-90-8339-895-2
This restricted web article provides an overview and selected extracts from the publication The Asset & Maintenance Management Lemniscate (ISBN/EAN 978-90-8339-895-2). It is made available exclusively to registered SSAMM Academy clients as part of their personal, non-transferable licence.
© 2024 Stoker / SSAMM. All rights reserved.
This content is provided under a personal, non-transferable licence. Unauthorised sharing of logins, screenshots, files or copies (in whole or in part) is not permitted
The landscape of Asset & Maintenance Management continues to evolve under the combined influence of digital transformation and rising expectations for human-centricity, resilience, and sustainability. A persistent challenge in practice is that organisations often apply asset management and maintenance standards in fragmented ways, resulting in weak traceability between strategic intent, cross-functional decision-making, and operational execution. The ISO 55000:2024 series frames alignment as a foundational principle of effective asset management and provides the normative basis for strengthening this traceability within an Asset Management System (AMS).
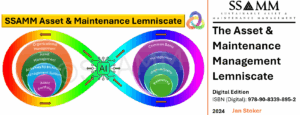
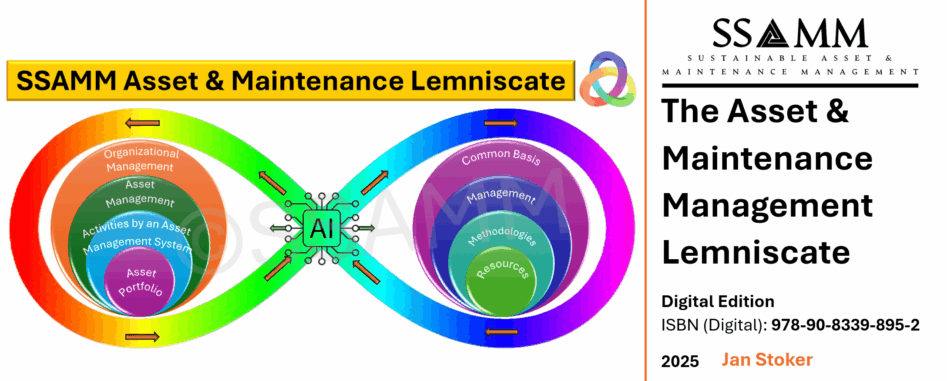
This article positions the lemniscate (∞) as a practical “line of sight” architecture and develops it through two complementary dimensions.
The Vertical Line of Sight is articulated as a governance mechanism that connects policy, strategy, lifecycle objectives, planning, execution, and structured feedback across hierarchical levels, enabling coherence and adaptability.
The Horizontal Line of Sight is developed as the cross-functional architecture that integrates maintenance, operations, engineering, finance, procurement, HSE, and data governance, strengthening maintainability, innovation, and lifecycle efficiency through shared objectives and shared information.
The integration of these dimensions is presented as the decisive maturity step that transforms alignment from a descriptive concept into an auditable, system-wide capability for lifecycle value creation. Within this integrated alignment view, Industry 5.0 and AI are positioned as human-centred enablers that enhance real-time visibility, decision support, and organisational learning, provided they are embedded in clear decision rights, robust data governance, and competence assurance.
The framework is anchored in the ISO 55000:2024 series, complemented by relevant European maintenance standards and the EFNMS Body of Knowledge, and is further supported by a concise integrator clause that links alignment to risk- and decision-quality discipline through the Asset Management BowTie, the P–C–R Trefoil Balance, and Value Chain Standardization. The resulting perspective offers a coherent basis for structuring, implementing, and assuring an AMS in maintenance-intensive organisations operating in an Industry 5.0 context
Application for A&MM Lemniscate inlog- Concept draft Asset Management Union Juni2 2014 Click Here
- Publication AM Union & Digital Line of Stight December 2015 Click Here
- Concept A&MM Lemniscate 2023
- Fisrst draft A&MM Lemniscate 19 februari 2024
- Updated 17 February 2025
- Updated 7 August 2025
Maintenance Fundamentals SAM, First Edition Keynote Āpōpō Congres 2026Follow Sustainable Asset Management for latest updates
Countdown SSAMM Academy Module 1
Explore the SSAMM Academy Asset Management and Maintenance Management courses.
Click Here for the Smart information page
Author: Ing. Jan Stoker MSc. MEng. AMCP. CFAM. Follow Jan Stoker
1. Lemniscate Cornerstones IAM Anatomy, ISO55000:2024, EFNMS BoK, and The AM-Bowtie
The lemniscate metaphor captures the central challenge of modern Asset & Maintenance Management: how to ensure demonstrable and lasting connectivity between strategic intent and operational reality while safeguarding lifecycle value. Its conceptual strength rests on four complementary cornerstones — the IAM Anatomy v4, the ISO55000:2024 (Click here for full Article), the EFNMS Body of Knowledge (BoK), and the Asset Management BowTie. Together they confirm that alignment is neither abstract nor optional: it is a normative requirement and a professional discipline.
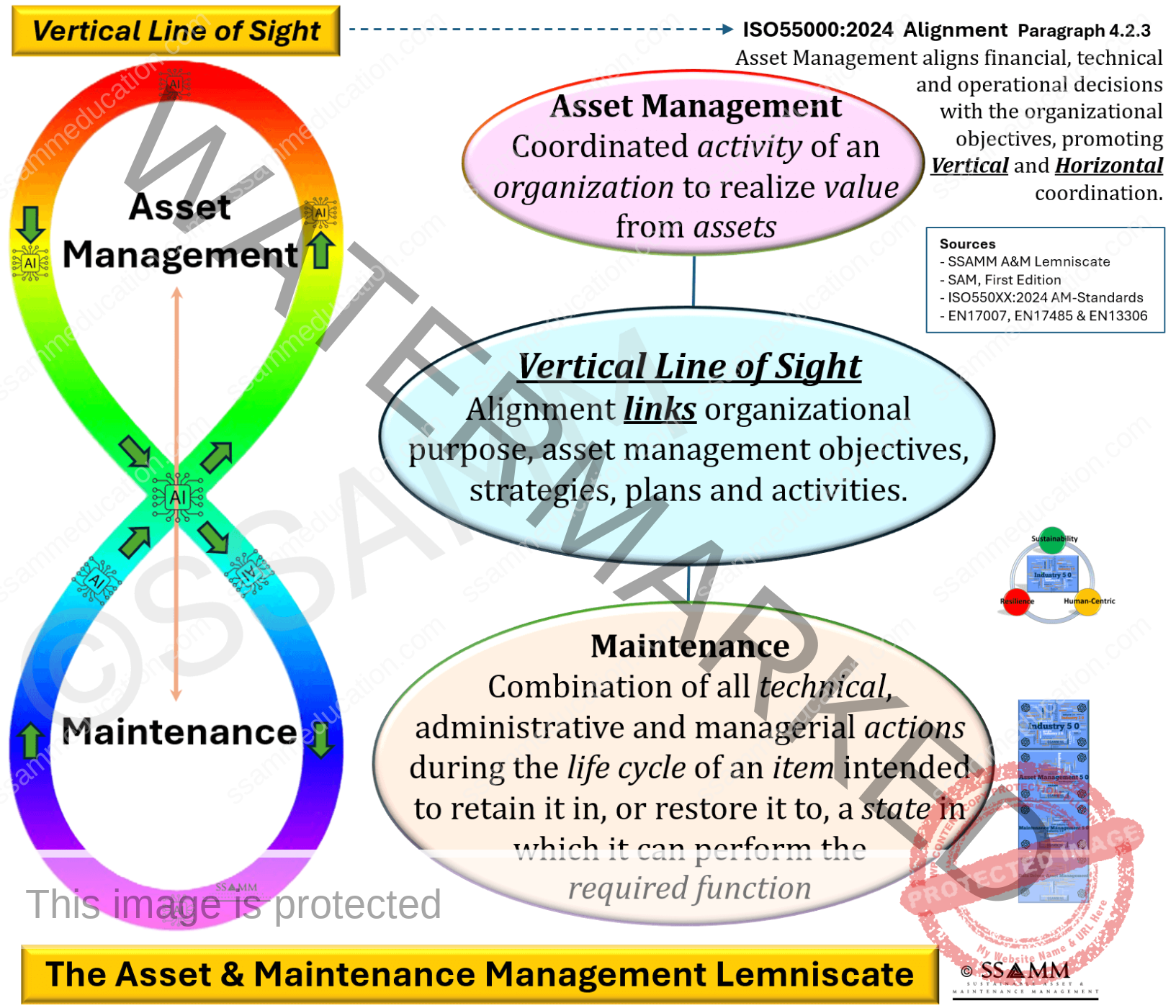
The ISO 55000:2024 series reinforces this imperative by defining Asset Management as a coordinated activity that realises value through the management of assets. Effective Asset Management is therefore not achieved through documentation or compliance rituals, but through consistent decision-making across financial, technical, and operational domains. Paragraph 4.2.3 explicitly states that organisational objectives must guide decisions at all relevant levels, providing the normative foundation for both vertical and horizontal coordination. The lemniscate becomes the interpretive device that translates this ISO principle into an organisational “line of sight” between purpose and practice.
The EFNMS BoK further strengthens this foundation by defining maintenance as a value-contributing discipline in its own right. Maintenance is the combination of technical, administrative, and managerial actions that prevent failures, restore functionality, and assure availability. This competence-based view complements the ISO logic: alignment is simultaneously a system requirement and a capability requirement. Without a shared professional language and harmonised competence expectations, the line of sight collapses.
Finally, the Asset Management BowTie operationalises this coherence by connecting threats, barriers, escalation factors, and recovery controls to strategic objectives. It provides a visual bridge between governance logic and risk-based operational control.
Collectively, these four cornerstones justify the lemniscate as a standards-anchored and competence-driven model that links alignment principles with audits, roles, and operational outcomes. They establish the conceptual basis for the refinement of vertical and horizontal alignment developed in subsequent chapters.
1.1 Vertical Alignment: The Vertical Lemniscate
Vertical alignment connects organisational purpose with operational execution by ensuring that intent, priorities, and decision criteria flow coherently from governance to the frontline. In asset-intensive environments this coherence is essential, as lifecycle cost, performance, and risk outcomes are shaped by decisions distributed across multiple layers. The Vertical Lemniscate is therefore not a linear cascade of directives but a closed governance loop in which strategy is translated into plans and operational experience feeds back into strategic refinement.
Such alignment maintains integrity between the organisation’s declared objectives and its actual behaviour. A common risk is that strategies appear aligned on paper while operational routines evolve locally under legacy constraints or reactive pressures. Vertical alignment mitigates this through traceability: objectives are made visible in lifecycle plans, maintenance policies, resource allocation, and work prioritisation. Within a mature AMS, objectives must not only exist but be demonstrably linked to decision frameworks that guide daily work.
Feedback from operational levels to senior leadership is equally critical. Beyond quantitative indicators, it must include contextual judgement, observed failure modes, human-factor insights, and supply-chain constraints. The Vertical Lemniscate thus functions as a structured learning mechanism, preventing strategy from drifting away from operational truth.
Within the Industry 5.0 paradigm, vertical alignment gains further depth through the human-centric principle. Operational professionals are recognised as informed contributors to strategy rather than executors of predefined tasks. AI and advanced analytics can strengthen this by providing real-time insight into asset condition and maintenance effectiveness. Yet digital intelligence adds value only when embedded within transparent accountability, defined decision rights, and systematic competence development. Vertical alignment in the Industry 5.0 sense therefore extends beyond efficient data flows toward responsible, human-supported governance coherence.
1.2 Horizontal Alignment: The Horizontal Lemniscate
Horizontal alignment concerns integration across departments, disciplines, and stakeholder interfaces that collectively determine asset value. Even with well-cascaded strategies, asset performance will remain suboptimal if silos create conflicting priorities or inconsistent interpretations of risk and cost. The Horizontal Lemniscate captures this organisational reality: Asset Management is intrinsically multidisciplinary and must be governed through shared objectives, language, and decision frameworks.
Deliberate collaboration mechanisms are needed to link maintenance, operations, engineering, finance, procurement, HSE, and data governance into one coherent value chain. This ensures that trade-offs are examined within a shared lifecycle logic. Procurement that neglects maintainability may yield short-term savings yet increase long-term risk; maintenance strategies detached from financial coherence can erode investment credibility. Horizontal alignment provides the structure through which such contradictions are reconciled via cross-functional prioritisation and shared accountability.
Industry 5.0 deepens this view by framing collaboration as both a resilience and a sustainability requirement. Human-centricity demands mutual respect for distinct expertise and transparent synthesis of evidence and professional judgement. Resilience requires that cross-functional responses can be mobilised rapidly during disruptions while maintaining coherence of purpose. Sustainability calls for lifecycle decisions that account for environmental and social implications — achievable only through integrated, multi-disciplinary evaluation.
AI systems can support horizontal alignment by providing unified data platforms and interoperable analytics that enhance shared situational awareness. However, these technologies depend on methodological and terminological consistency, a principle enshrined in CEN/TC 319 standards such as EN 13306 (terms) and EN 17007 (processes & indicators). The Horizontal Lemniscate thus represents both a cultural and structural discipline: alignment is achieved when interaction patterns, data definitions, and decision criteria are standardised and applied consistently across all functions.
1.3 The Full Lemniscate: Holistic Alignment
The full lemniscate symbolises holistic alignment as prescribed by ISO 55000:2024 and reinforced by the IAM and EFNMS frameworks. It integrates both vertical and horizontal loops into a single organisational architecture for lifecycle value creation. The figure-eight form signifies reciprocity and continuity: strategic direction flows downward while operational intelligence flows upward, and functional collaboration occurs laterally across the loop.
These movements must remain balanced to sustain performance, cost control, and risk governance. Continuous circulation within the lemniscate embodies the essence of continual improvement — essential for organisations managing long-lived, high-consequence assets. The model also cautions against partial maturity: strong vertical governance without cross-functional integration can yield coherent strategy but poor execution; conversely, vibrant collaboration without strategic anchoring may create local optimisation without portfolio coherence. Holistic alignment requires both.
Industry 5.0 and AI extend this dynamic by ensuring that technological progress strengthens both dimensions simultaneously. Predictive analytics can inform strategic investment timing while shared digital environments enhance cross-functional coherence. Yet human-centric governance ensures that technology augments, rather than replaces, professional responsibility and judgement.
In this configuration, the lemniscate becomes more than a metaphor; it functions as a unifying interpretive architecture that connects standards, competence frameworks, and performance-cost-risk logic. It operationalises the principle that alignment is a living system — one that evolves through accountable roles, structured learning, and the disciplined integration of data, technology, and human capability.
Consequently, the lemniscate provides the conceptual gateway to the deeper elaboration of the Vertical and Horizontal Lines of Sight in Chapter 2 and the contextual embedding of Industry 5.0 implementation pathways explored in Chapters 3 and 4. It represents the visual and intellectual synthesis of Asset Management as a system of alignment — governed by standards, enabled by competence, and sustained through learning.
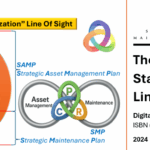
2. The Horizontal & Vertical line of sight: Deepening the subject
This chapter deepens both concepts in relation to the ISO 55000:2024 series (with emphasis on ISO 55001:2024, ISO 55002:2024, ISO 55010:2024, and ISO 55013:2024) and the European maintenance standards that structure competence, process and governance (including EN 15628, EN 17007 and EN 17485). It also positions these alignment mechanisms within an Industry 5.0 setting in which human-centricity, resilience and sustainability must be demonstrably integrated into the Asset Management System (AMS).
2.1 The Vertical Line of Sight: Strategic Alignment Across Levels
The Vertical Line of Sight forms one of the two foundational dimensions of the lemniscate-based alignment logic. It connects long-term organisational intent with the day-to-day execution of asset-related and maintenance-related activities, thereby creating traceability between strategic ambition, governance decisions, resource allocation and operational outcomes. Interpreted through the ISO 55000:2024 lens, vertical alignment is the structured translation of organisational context and stakeholder expectations into the AMS, and subsequently into coherent policies, plans, maintenance strategies and execution regimes.
2.1.1 Strategic Governance and Policy Frameworks
At the top of the vertical architecture lies strategic governance, typically led by executive leadership and the Asset Manager in structured engagement with internal and external stakeholders. Guided by ISO 55000:2024 and formalised through ISO 55001:2024 requirements, this layer articulates why assets exist within the organisational purpose, what value they must create, and which boundaries of safety, risk and sustainability must be respected. A credible Vertical Line of Sight begins when these expectations are translated into an Asset Management policy and a coherent set of strategic objectives that are designed for operational translation, not only for symbolic reassurance. EN 17485 can be interpreted as a reinforcing governance architecture that clarifies responsibilities and embeds the expectation that maintenance governance is inseparable from asset governance.
A mature policy framework therefore describes decision rights, escalation routes, and the conditions under which objectives can be recalibrated based on evidence. For asset portfolios characterised by long lifetimes, high-consequence risks and constrained budgets, this top layer must also be explicitly sensitive to asset criticality, lifecycle stage and societal obligations. The BowTie logic can function here as an interpretive tool that connects strategic risk appetite to preventive and corrective control philosophies in a way that is transparent and defensible.
2.1.2 Translating Strategy into Operational Actions
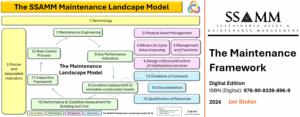
The second component of vertical alignment is the formal and practical conversion of strategic intent into operationally meaningful actions. In maintenance-intensive settings, this translation is commonly enacted by the Maintenance Manager and Maintenance Engineer, whose responsibilities and competence expectations are articulated in EN15628:2024 (Click here for full Article).
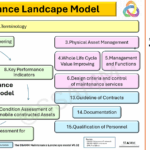
The Maintenance Landscape Model provides an operational architecture for the right-hand side of the lemniscate by structuring maintenance processes and interfaces so that strategy does not dissolve into localised, inconsistent practices. In line with the Value Chain Standardization Line of Sight, this translation layer is also strengthened when language, methods and data definitions are harmonised across the value chain. Consistent failure coding, performance thresholds, asset hierarchy rules and maintenance-type taxonomies reduce interpretive drift and make strategic directives resilient to organisational complexity.
2.1.3 Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement
A robust Vertical Line of Sight is characterised by structured feedback loops that transform the vertical dimension into a learning system rather than a one-way cascade. Reliability data, work history, condition information, incident patterns and operational deviations constitute evidence that must inform strategic review cycles, risk reassessment and reprioritisation. The logic of management system maturity implies that performance monitoring is not a passive reporting function but a mechanism for disciplined adjustment. ISO 55010:2024 reinforces this expectation by emphasising alignment of Asset Management with broader organisational decision frameworks, including financial governance and investment logic.
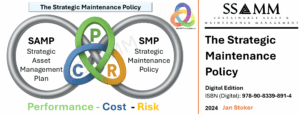
Frontline leadership, including Maintenance Supervisors and operational team leads, are critical carriers of interpretive evidence because they can explain not only what occurred but why deviations emerged and which systemic barriers impeded performance. The Industry 5.0 emphasis on human-centricity adds a qualitative requirement to these loops: feedback systems must respect professional judgement and tacit knowledge and ensure that digital tools amplify rather than replace practitioner insight. The P–C–R oil Balance can serve as a structured language for escalation and recalibration, allowing operational signals to be translated into explicit proposals for shifting dominance among Performance, Cost and Risk without eroding alignment integrity.
2.1.4 Technology as a Catalyst for Vertical Alignment
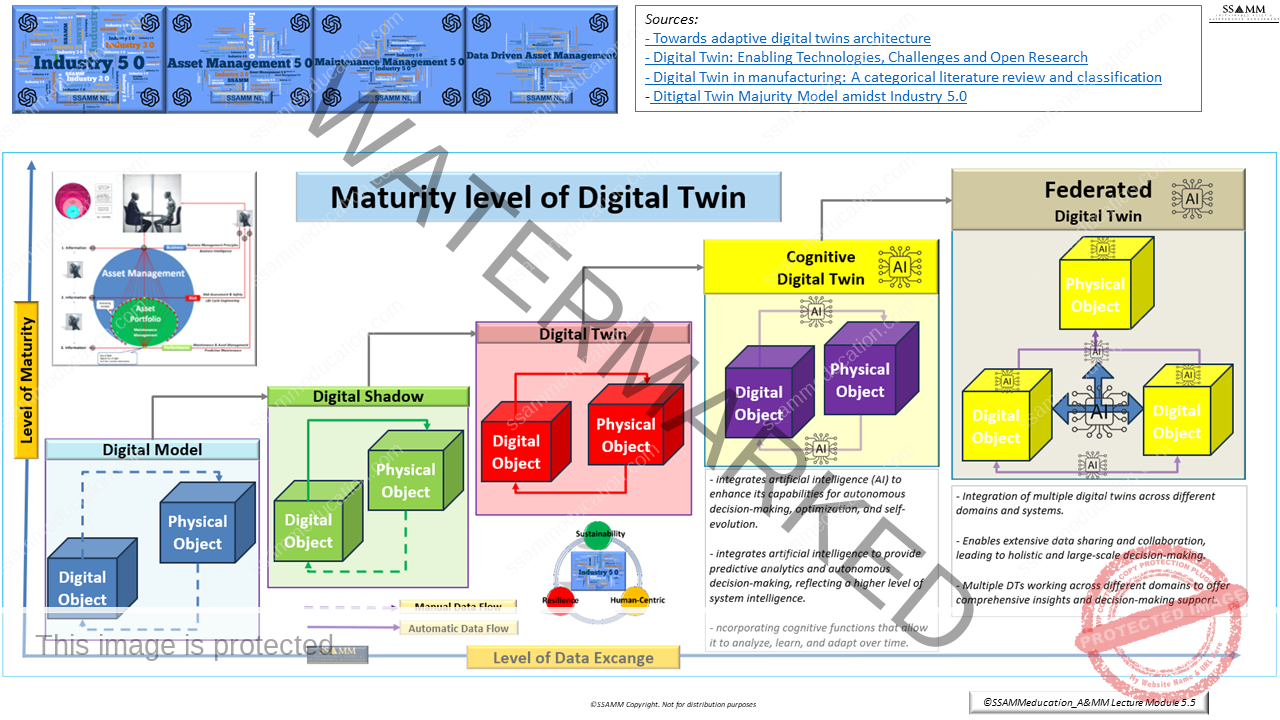
Emerging technologies increasingly function as accelerators of vertical coherence by reducing latency between operational reality and strategic awareness. Digital Twins, IoT-enabled monitoring and AI-based analytics can enable earlier detection of performance degradation, improved prediction of failure trajectories and more consistent prioritisation of interventions. When integrated under the guidance of ISO 55012:2024 and governed through ISO 55013:2024, such technologies strengthen a data-informed AMS that makes vertical decision-making transparent and auditable.
The core value of technology in vertical alignment is therefore not synonymous with automation alone, but with the creation of a unified evidence base shared across hierarchical levels. This requires explicit rules for data ownership, quality assurance and interoperability. It also requires that digitalisation is governed as part of the AMS rather than as a parallel transformation agenda. In an Industry 5.0 context, AI-enabled predictive maintenance must remain embedded in human-accountable decision processes, with interpretability and explainability aligned to risk logic and value intent.
Properly governed, technology becomes a catalyst for the BowTie’s preventive and corrective logic, supporting a clearer line of sight between strategic risk appetite, barrier performance and operational intervention choices.
2.2 The Horizontal Line of Sight: Interdepartmental Synergy
While vertical alignment ensures coherence across organisational levels, the Horizontal Line of Sight addresses the integration of functions that collectively shape lifecycle value. Maintenance outcomes are rarely produced within one discipline. Instead, they emerge from the interaction of operations, engineering, finance, procurement, HSE, sustainability and data governance with maintenance as an essential contributor to reliability and resilience. The Horizontal Line of Sight is thus the mechanism through which specialist domains are connected into shared objectives, shared decision logic and shared accountability.
Within the ISO 55000:2024 series, this dimension can be interpreted as a foundational condition for an effective AMS: without explicit management of cross-functional dependencies, alignment becomes fragmented by design. The Industry 5.0 principles deepen this necessity. Human-centricity requires respectful integration of expertise and clarity of purpose across boundaries. Resilience requires the capacity for cross-functional response without excessive sequential escalation. Sustainability requires that lifecycle decisions reflect system-wide environmental and social consequences rather than narrow functional optimisation. The CEN/TC 319 standards strengthen horizontal alignment by providing shared terminology (EN 13306), standardised process and indicator logic (EN 17007) and governance principles that integrate maintenance in organisational decision architectures (EN 17485).
2.2.1 Interdepartmental Collaboration for Shared Goals
The first operational pillar of horizontal alignment is structured collaboration around shared Asset Management objectives. The Horizontal Line of Sight does not merely encourage cooperation; it defines how responsibilities, resources and decision rights are distributed and coordinated so that each function can trace its daily choices back to a common value logic. ISO 55002:2024 underlines that alignment is achieved through explicit design of interfaces, not through broad declarations of teamwork.
Maintenance priorities must reflect operational performance requirements and risk tolerances. Procurement strategies must incorporate maintainability, reliability and total lifecycle cost rather than short-term unit-price optimisation. Financial planning must be able to represent the risk-reducing value of preventive maintenance and the long-term efficiency of reliability-driven investments. Role logic from EN 15628 can be read as a practical enabler here: the Asset Manager sustains strategic coherence, while Maintenance Managers and Maintenance Engineers integrate operational and technical perspectives across function boundaries. In a mature horizontal architecture, cross-functional forums and joint decision pathways strengthen ownership without dissolving accountability, thereby protecting the integrity of the lemniscate’s connective intent between Asset Management “left-hand” governance and maintenance “right-hand” execution.
2.2.2 Data Sharing and Integrated Insights
Shared data constitutes the informational backbone of horizontal alignment, especially in increasingly digital asset environments. ISO 55013:2024 positions data as a strategic asset that requires governance of quality, accessibility and accountability. For maintenance-intensive organisations, this is not abstract doctrine. Maintenance Engineers require reliable condition and operational data to optimise intervention strategies. Asset Managers require coherent lifecycle cost and risk data to refine investment logic. Operations require transparent maintenance forecasts to manage service performance and operational scheduling. Without standardised definitions of failure modes, performance thresholds and asset hierarchies, data sharing becomes a generator of misalignment. The Value Chain Standardization perspective becomes directly relevant: harmonising language, process taxonomies and data definitions across the value chain strengthens the Horizontal Line of Sight by reducing interpretive variance across functions.
Technologies such as IoT platforms, cloud analytics and AI-driven pattern recognition enable integration, but their effectiveness remains dependent on governance maturity, including data collection rules, reporting alignment and shared criteria for fitness-for-purpose. In this sense, ISO 55013:2024 and the CEN/TC 319 standards jointly support the construction of an integrated information environment in which horizontal collaboration becomes evidence-based rather than assumption-driven.
2.2.3 Enhancing Maintainability and Lifecycle Efficiency
A critical contribution of horizontal alignment is the improved integration of maintainability into upstream and midstream lifecycle decisions. ISO 55001:2024 and the process logic of EN 17007 imply that maintainability is not a late-stage operational concern; it is a lifecycle property shaped by design choices, engineering standards, procurement specifications and operational regimes. The Horizontal Line of Sight ensures that maintenance expertise is structurally embedded in these earlier decisions.
Maintenance Supervisors and technical specialists can provide formalised feedback to engineering and procurement about failure patterns, component accessibility, standardisation opportunities and competence implications. When these insights are systematically translated into asset design and renewal decisions, the organisation reduces future maintenance burden, improves safety conditions and strengthens reliability outcomes. This aligns with the long-term stewardship logic of ISO 55011:2024, which emphasises value creation under societal, intergenerational and resource constraints. Within the Maintenance Landscape Model, this aspect can be understood as a disciplined interface among lifecycle planning, maintenance strategy development, work management and performance evaluation, ensuring that maintainability is treated as an organisational design requirement rather than an isolated technical aspiration.
2.2.4 Driving Innovation and Sustainability
The Horizontal Line of Sight also functions as a catalyst for innovation and sustainability by enabling the integration of diverse expertise into coherent solution pathways. Contemporary advances in asset and maintenance management often arise where disciplines intersect: reliability engineering combined with advanced analytics, circular design integrated with condition-based strategies, and human-centred work design supported by digital tools. ISO 55000:2024 frames sustainable value creation as a lifecycle obligation that balances economic, environmental and social outcomes.
Such balancing is inherently cross-functional. Industry 5.0 intensifies this requirement by emphasising that innovation should enhance professional agency, strengthen adaptive capacity and deliver measurable sustainability gains. A practical manifestation is the development of predictive maintenance programs co-designed by maintenance, operations, finance, HSE, sustainability and data governance rather than “owned” by a single function. The Horizontal Line of Sight provides the governance logic that connects performance targets, lifecycle cost rationales and risk constraints into one shared evaluation grammar. In doing so, horizontal alignment not only reduces coordination loss but actively increases the quality of strategic and operational innovation, ensuring that new solutions are legitimate, scalable and resilient across the organisational system.
2.3 Integrating Vertical and Horizontal Dimensions for Holistic Alignment
The decisive step from conceptual alignment to system-wide coherence lies in the explicit integration of vertical and horizontal dimensions into one governing architecture. When separately pursued, vertical alignment can connect strategy to execution, while horizontal alignment can enhance cross-functional collaboration. Mature Asset Management Systems, however, require both dimensions to be mutually reinforcing. In such an integrated interpretation, the lemniscate becomes a structural representation of how intent, risk governance, resource allocation, technical practice and performance learning remain continuously connected across levels and functions.
This integrated view aligns with the intent of the ISO 55000:2024 series: ISO 55001:2024 defines demonstrable alignment requirements, ISO 55002:2024 supports contextual tailoring, and ISO 55010:2024 and ISO 55011:2024 connect Asset Management to organisational decision frameworks, financial governance and long-term stewardship. The CEN/TC 319 standards provide complementary operational grammar by standardising terminology, processes and governance expectations. For maintenance-intensive organisations, this integrated architecture is not optional. Performance, cost and risk outcomes are inherently multi-factorial; cross-functional synchronisation without strategic anchoring lacks legitimacy, while strategic priorities without cross-functional integration lack delivery capacity.
2.3.1 Synergizing Strategic and Operational Goals
A first integrative outcome of combining vertical and horizontal alignment is the formation of a single, shared system of strategic and operational goals. ISO 55001:2024 and ISO 55010:2024 stress that Asset Management objectives must be embedded within the organisation’s broader decision architecture, implying co-ownership across the functional domains that shape operational reality. This requires explicit translation chains that preserve intent and prevent local reinterpretation. Strategic lifecycle value goals should be converted into asset class strategies, maintenance policies and resource plans that are jointly validated by maintenance, operations, engineering and finance. Such co-validation improves feasibility and reduces the risk that maintenance interventions become reactive responses to locally dominant pressures. Integration also depends on shared evaluation criteria.
A common failure pattern is that functional metrics compete, generating partial optimisation. The integrated Lines of Sight address this by deriving operational indicators and cross-functional targets from a shared value and risk logic. The Maintenance Landscape Model can support this structured derivation by mapping how maintenance system building blocks, interfaces and role responsibilities connect to strategic objectives, thereby strengthening demonstrability of alignment within the AMS.
2.3.2 Leveraging Technology for Unified Alignment
A second integrative mechanism is the deployment of technology as a unifying infrastructure for shared situational awareness and consistent interpretation. Digital Twins, IoT monitoring, advanced analytics and AI-based decision support can create a common operational picture for strategy, operations, maintenance and finance. ISO 55012:2024 supports embedding such technologies within AMS governance, while ISO 55013:2024 formalises the expectation that data is governed as a strategic asset with defined ownership, quality standards and lifecycle accountability.
However, this benefit remains conditional on standardisation of asset hierarchies, failure coding, performance thresholds and information models. The Value Chain Standardization Line of Sight complements this requirement by framing standardisation of language, processes, roles, methods and data definitions as the enabling logic that makes digital solutions integrative rather than silo-reinforcing.
2.3.3 Supporting Organizational Adaptability
A third integrative benefit is strengthened organisational adaptability, a core capability in the Industry 5.0 paradigm. Asset-intensive organisations must respond to emerging risks, technological shifts, regulatory expectations and evolving stakeholder priorities without losing coherence in governance and delivery. ISO 55011:2024 reinforces the expectation that long-term value creation must be safeguarded under uncertainty, positioning adaptability as an indicator of maturity rather than a deviation from discipline. Integrated vertical and horizontal alignment provides the governance scaffolding for such adaptation. Changes in risk appetite, budgetary constraints or performance expectations can be translated rapidly into updated cross-functional priorities and operational plans while preserving traceability.
At the operational level, learning loops become more powerful when technical insights are escalated vertically and interpreted horizontally, enabling timely adjustment of lifecycle plans. Industry 5.0’s human-centric emphasis implies that professional judgement and frontline experience must remain visible in these accelerated cycles, especially when AI is used to propose intervention priorities. Alignment maturity is therefore evidenced by the organisation’s capacity to adjust decisively without losing shared logic.
2.3.4 Enabling Value Creation Across the Asset Lifecycle
Ultimately, the integrated Lines of Sight are justified by their capacity to enable consistent, demonstrable value creation across the full asset lifecycle. ISO 55013:2024 highlights that aligning data assets with organisational goals strengthens decision quality and resource optimisation. Combined with the requirement logic of ISO 55001:2024 and the process and governance architecture embedded in CEN/TC 319 standards, this forms a robust foundation for performance stability, risk control and lifecycle cost efficiency. The integration also provides space for explicit decision discipline.
The P–C–R Trefoil Balance can be positioned at the conceptual crossing point of the lemniscate, where vertical priorities and horizontal dependencies frequently intersect. By formally declaring temporary dominance of Performance, Cost or Risk within defined constraints, organisations can replace ambiguous trade-off rhetoric with documented, defensible and auditable decisions. This strengthens alignment integrity over time because the rationale behind prioritisation remains traceable across levels and functions, enabling structured learning and refinement. In this integrated architecture, the Vertical and Horizontal Lines of Sight become a coherent line-of-sight system that operationalises the combined intent of the ISO 55000:2024 series, the IAM alignment logic and the European maintenance standards, while positioning the organisation for resilient, sustainable and human-centred value delivery in an Industry 5.0 landscape.
3. Industry 5.0: Human-Centric, Resilience, and Sustainability
Industry 5.0 represents a deliberate recalibration of industrial and technological development. It builds on the automation, connectivity, and cyber-physical integration of Industry 4.0, while explicitly re-centring the human being, societal value, and ecological boundaries as decisive parameters for industrial progress. For asset-intensive organisations, this shift is not merely conceptual; it reframes how Asset & Maintenance Management should be governed, designed, and assured under conditions of increasing complexity, uncertainty, and societal scrutiny.
Consequently, the purpose of the Asset Management System (AMS) as described in the ISO 55000:2024 series is deepened: value creation must be defined and evidenced not only in terms of technical performance and financial efficiency, but also in terms of workforce capability, organisational learning, ethical and safe decision-making, and sustainable lifecycle outcomes.
Enabling technologies such as AI, advanced analytics, Industrial IoT, and Digital Twins therefore need to be interpreted through a governance lens rather than treated as autonomous technical solutions. Industry 5.0 does not reject automation; it requires that digital intelligence demonstrably serves human empowerment, robust service continuity, and responsible resource use across the full asset lifecycle. The Industry 5.0 lens also aligns with the Maintenance Landscape logic and the use of common basis standards such as EN 13306 for shared terminology and EN 17007 for process and indicator coherence, thereby reducing fragmentation between strategic intent and operational practice.
3.1 Human-Centric Approaches
A human-centric orientation within Industry 5.0 positions people as active co-creators of value rather than passive recipients of technological change. In Asset & Maintenance Management, this requires the deliberate design of systems, processes, and technologies that enhance professional judgement, reduce unnecessary cognitive load, strengthen safety and wellbeing, and support meaningful competence development. Within the Vertical Line of Sight, human-centricity reinforces the principle that strategic objectives, asset policies, and lifecycle plans must incorporate explicit assumptions about workforce capacity, skills evolution, and the human implications of asset risk profiles. This connects to the role and competence logic of EN 15628, where clarity of responsibilities and demonstrable competence are prerequisites for reliable execution. Within the Horizontal Line of Sight, human-centricity implies cross-functional decision spaces in which maintenance, operations, engineering, HSE, procurement, and digital specialists interpret evidence using a shared language and mutually respected expertise, supported by harmonised terminology and process structures from the CEN/TC 319 standards.
AI and analytics can reinforce this ambition when deployed as decision support rather than decision replacement. Predictive alerts and Digital Twin scenarios can extend human situational awareness, but the human-centric principle requires explainability, transparent accountability, and the maintained authority of practitioners to validate, contextualise, and, when risk demands, override algorithmic advice. Human-centric alignment also requires that feedback loops are treated as professional knowledge routes; frontline experience should systematically inform the refinement of asset strategies and the calibration of risk-control rationales.
3.2 Resilience
Building resilience within Asset & Maintenance Management systems is essential for organisations that must sustain service delivery under disruptive conditions, including climate impacts, supply-chain volatility, cyber-physical incidents, and rapid demand shifts. Industry 5.0 frames resilience as a proactive and systemic capability: the ability to anticipate vulnerabilities, absorb shocks, adapt operations, and recover performance without compromising safety, public obligations, or long-term value. From a vertical alignment perspective, resilience requires that governance explicitly articulates risk appetite, criticality logic, and recovery expectations across asset portfolios, and that these are embedded in asset strategies and maintenance policies.
The Asset Management BowTie offers a structured bridge by connecting threats, preventive barriers, escalation factors, and recovery controls to strategic intent and operational capability. From a horizontal alignment perspective, resilience depends on the organisation’s ability to mobilise integrated responses across functions and supply networks. Standardised processes and indicators, such as those outlined in EN 17007, can strengthen contingency planning and evidence-based response decisions. AI and real-time monitoring can accelerate resilience only when data governance ensures an integrated and trusted condition and context dataset for cross-functional interpretation and learning. Practically, this implies joint scenario planning, disciplined learning reviews, and resilience-oriented resource strategies for critical spares and specialist capabilities that can be mobilised across organisational and supplier boundaries.
3.3 Sustainability
Sustainability is a defining principle of Industry 5.0 and a decisive horizon for contemporary Asset & Maintenance Management. It expands lifecycle value beyond short-term operational or financial optimisation toward responsible stewardship of resources, emissions, safety outcomes, and broader social impacts across long-lived asset systems. For maintenance-intensive organisations, sustainability is inseparable from decisions on renewal timing, life extension, reliability investment, spare-parts strategies, and the balance between preventive, predictive, and corrective interventions.
In the vertical alignment dimension, sustainability must be reflected in strategic objectives and asset policies that translate long-term environmental and social constraints into measurable expectations at portfolio and asset-class level, aligned with the ISO 55000:2024 system logic. In the horizontal alignment dimension, sustainability depends on the consistent integration of specialist viewpoints across the value chain: procurement aligned with circularity and maintainability, engineering embedding energy and material efficiency in design and modification, and maintenance providing evidence on failure behaviour and real-world component lifetime to support informed replacement versus life-extension choices.
Advanced analytics can support sustainable outcomes by optimising intervals, reducing unnecessary work, and improving renewal timing, but Industry 5.0 insists that these gains are achieved in a human-centred way that also strengthens working conditions, competence, and organisational learning. Where circular-economy ambitions are present, maintenance data on condition, repairability, and obsolescence becomes a strategic input for design-for-maintainability and end-of-life decisions, strengthening both compliance and societal legitimacy.
4. Practical Implementation and Integration
Building on the alignment architecture established in Chapter 2 and the Industry 5.0 principles outlined in Chapter 3, this chapter translates conceptual coherence into actionable implementation. The Vertical and Horizontal Lines of Sight define what mature, standards-aligned Asset & Maintenance Management should achieve, while Industry 5.0 clarifies why this maturity must be human-centric, resilient, and sustainable. The central question is therefore how organisations can embed these principles into capability building, operational routines, and governance mechanisms that are both scalable and auditable within an Asset Management System (AMS).
Implementation requires deliberate harmonisation of roles, processes, methods, and data throughout the Asset & Maintenance Management value chain. The ISO 55000:2024 series provides the overarching management system framework, while the CEN/TC 319 standards deliver the operational backbone for terminology, process architecture, and maintenance governance. Within this dual normative structure, successful implementation cannot be reduced to the adoption of digital tools. Technologies such as AI, Digital Twins, and IoT-based monitoring generate sustainable value only when embedded within coherent decision rights, data governance, and competence expectations. Implementation is therefore an organisational transformation supported by technology, not a technology project with incidental human consequences.
This chapter focuses on the practical conditions required to operationalise the integrated line-of-sight model: competence development and role clarity, professional knowledge systems such as the EFNMS Body of Knowledge (BoK), and the controlled incorporation of innovation within a standards-aligned AMS. It also recognises the organisational challenges that can undermine integration—fragmentation, data inconsistency, and insufficient human-centred governance.
4.1 Training and Certification
Embedding Industry 5.0 principles and AI capabilities within Asset & Maintenance Management is ultimately a people-driven transformation. Even the most advanced architectures—such as the Vertical and Horizontal Lines of Sight—depend on disciplined competence development, clearly defined roles, and a shared professional language. The ISO 55000:2024 series indirectly implies this through its emphasis on leadership, planning, and continual improvement, but the requirement becomes explicit when European maintenance standards are applied to operationalise roles and performance expectations along the right-hand side of the lemniscate.
The EFNMS Body of Knowledge provides a structured competence foundation for this purpose. By defining maintenance as a combination of technical, administrative, and managerial actions, it forms a bridge between the strategic intent of Asset Management and the operational disciplines needed for reliability and safe continuity. When interpreted alongside EN 15628, training and certification can serve as organisational assurance: the competence of Asset Managers, Maintenance Managers, and Engineers must be demonstrable and auditable within the AMS.
A structured training and certification pathway strengthens vertical alignment by ensuring that strategic objectives are executed by professionals who understand lifecycle logic, risk-based maintenance, and the governance requirements of the AMS. It also supports horizontal alignment by fostering a shared understanding among maintenance, operations, engineering,
procurement, HSE, finance, and digital domains. In this sense, competence development becomes the operational foundation for Value Chain Standardization, because consistent language, methods, and decision criteria cannot exist without systematic professional education.
Within the Industry 5.0 context, human-centricity adds further depth. Training must extend beyond technical expertise to include ethical reasoning, cross-functional communication, and the ability to interpret AI recommendations critically. The objective is the creation of “augmented professionals” who can combine analytical outputs with contextual judgement. In predictive maintenance and Digital Twin environments, success depends less on algorithmic accuracy than on human capability to validate, contextualise, and integrate digital insights into operational decisions. Certification thus becomes not only a validation of competence but also a mechanism for accountability and assurance within the AMS.
4.2 Future Trends and Innovations
The next development phase of Asset & Maintenance Management will be defined by deeper integration of digital intelligence into lifecycle governance. Innovations in AI-enabled predictive maintenance, advanced condition monitoring, and Digital Twin maturity will progressively reshape how alignment and decision-making occur. When applied coherently within the intent of ISO 55012:2024, these technologies can accelerate vertical and horizontal integration by improving the speed, accuracy, and transparency of decisions. Their real strategic value lies in reducing lifecycle uncertainty, strengthening risk-based prioritisation, and improving the reliability of performance forecasting.
Human–machine collaboration will increasingly become a deliberate design principle. Future systems will be evaluated not only by their technical capability but by their contribution to safer work, improved knowledge transfer, and more resilient behaviour. For instance, AI-driven decision dashboards may connect strategic objectives, asset criticality, and work priorities in one interface—thereby operationalising the line-of-sight model and making strategic rationale visible at every organisational level.
Emerging technologies may also expand the governance scope of the AMS. Distributed ledger concepts such as blockchain can enhance assurance by ensuring the traceability of maintenance histories, spare parts provenance, and compliance evidence across extended supply chains. Likewise, augmented and virtual reality can enrich competence development by providing safe, immersive training environments for complex maintenance tasks. These tools become strategically valuable only when integrated within role expectations and competence frameworks such as EN 15628 and the EFNMS BoK.
From a data governance perspective, ISO 55013:2024 emphasises that the strategic value of innovation depends on data integrity, accessibility, and ownership. The future digital AMS must therefore function as an integrated information ecosystem rather than a collection of disconnected tools. The maturity of Value Chain Standardization—shared language, harmonised process taxonomies, and defined data structures—determines whether innovation can scale safely. In essence, standardisation provides the architecture within which innovation can flourish.
4.3 Challenges and Considerations
Although the benefits of integrating Industry 5.0 and AI into Asset & Maintenance Management are substantial, implementation remains complex. The most persistent challenge is organisational fragmentation: adopting technologies or partial standards in isolation can create parallel systems that erode the integrity of the line-of-sight architecture. Large, asset-intensive organisations are particularly vulnerable, given entrenched functional autonomy and legacy infrastructures. The integration imperative of the ISO 55000:2024 series therefore demands strong governance oversight to ensure that digital initiatives, training programmes, and process redesigns are explicitly anchored in the AMS.
A second challenge involves data integrity and interpretability. AI and predictive systems are only as reliable as the data that feeds them. Inconsistent asset hierarchies, poor failure coding, and incomplete maintenance histories can produce misleading insights, compromising alignment and risk control. ISO 55013:2024 thus becomes a key assurance instrument, positioning data governance as a central Asset Management responsibility rather than a technical afterthought.
The human dimension poses a third challenge. Industry 5.0 rejects the notion of passive workforce adaptation; instead, it requires competence development, role clarity, and trust in technology-supported decision-making. Organisations must avoid skills polarisation and ensure that automation enhances rather than diminishes professional autonomy. Investment in AI literacy, reliability engineering, and cross-functional collaboration is therefore essential. Frameworks such as EN 15628 and the EFNMS BoK provide the foundations for structured competence pathways that integrate human-centred learning into technological transformation.
Finally, accountability and ethics require explicit attention. As algorithmic recommendations influence decisions, clear decision rights and oversight must remain embedded in the AMS. Human validation should always be present, with transparent criteria for when digital advice is accepted or overridden. This principle resonates with the lemniscate’s governance balance and the P–C–R Trefoil logic: in the tension between performance, cost, and risk, decisions must follow an explicit, auditable rationale. Only through such disciplined governance can Industry 5.0 evolve from a technological promise into a credible, human-centred advancement of Asset & Maintenance Management practice.
5. Wrap up
This abstract has positioned the lemniscate as a robust alignment metaphor and a practical governance logic for contemporary Asset & Maintenance Management. In line with the ISO 55000:2024 series and reinforced by the IAM Anatomy and relevant CEN/TC 319 standards, the core argument is that sustainable lifecycle value depends on the simultaneous strength of a Vertical Line of Sight (strategy-to-execution coherence) and a Horizontal Line of Sight (cross-functional integration). When these two dimensions are deliberately integrated, the Asset Management System (AMS) becomes a coherent, auditable architecture rather than a collection of partial standards, local practices, or isolated digital initiatives.
Within this integrated alignment view, the Asset Management BowTie clarifies the link between value, risk, and preventive/corrective control logic, while the P–C–R Trefoil Balance provides a disciplined language for transparent prioritisation when performance, cost, and risk tensions arise. The Value Chain Standardization Line of Sight further strengthens implementation by emphasising the standardisation of language, roles, processes, methods, data, and competence across the full Asset & Maintenance Management chain, reducing interpretive drift and enabling repeatability at scale.
Industry 5.0 frames these alignment requirements as human-centric, resilient, and sustainable obligations. AI, Digital Twins, and IoT can accelerate and deepen the line-of-sight architecture, but only when embedded in clear decision rights, robust data governance, and structured competence development. The EFNMS Body of Knowledge and EN 15628 role logic provide essential foundations for this professionalisation.
In conclusion, the future-ready AMS in maintenance-intensive organisations is best understood as a multi-dimensional alignment system that integrates strategy, cross-functional execution, risk-informed decision logic, data governance, and human capability. By operationalising these principles, organisations can strengthen reliability, improve maintainability, enhance resilience, and deliver sustainable lifecycle value in an increasingly complex Industry 5.0 environment.
Tags: Newsletter 1