Publication reference
Title: Maintenance Engineering. Future Proof Maintenance Engineering, First Edition
Author: Benjamin Stoker
Publisher: SSAMM (Click Here)
Publication platform: SSAMM Academy – ssammeducation.com
ISBN/EAN: 978-90-8339-898-3
This restricted web article provides an overview and selected extracts from the publication Building an Asset Management System (AMS) (ISBN/EAN 978-90-8339-894-5). It is made available exclusively to registered SSAMM Academy clients as part of their personal, non-transferable licence.
© 2024 Stoker / SSAMM. All rights reserved.
This content is provided under a personal, non-transferable licence. Unauthorised sharing of logins, screenshots, files or copies (in whole or in part) is not permitted
Maintenance Engineering has evolved from being a purely technical discipline to a strategic enabler of organizational success. In The Industry 5.0 era, where human-centricity, sustainability, and technological integration redefine industrial practices, maintenance engineering plays a pivotal role in ensuring that physical assets perform reliably, efficiently, and sustainably throughout their lifecycle. The shift from reactive to proactive and strategic maintenance requires a deeper alignment with asset management principles and an adherence to robust frameworks and standards.
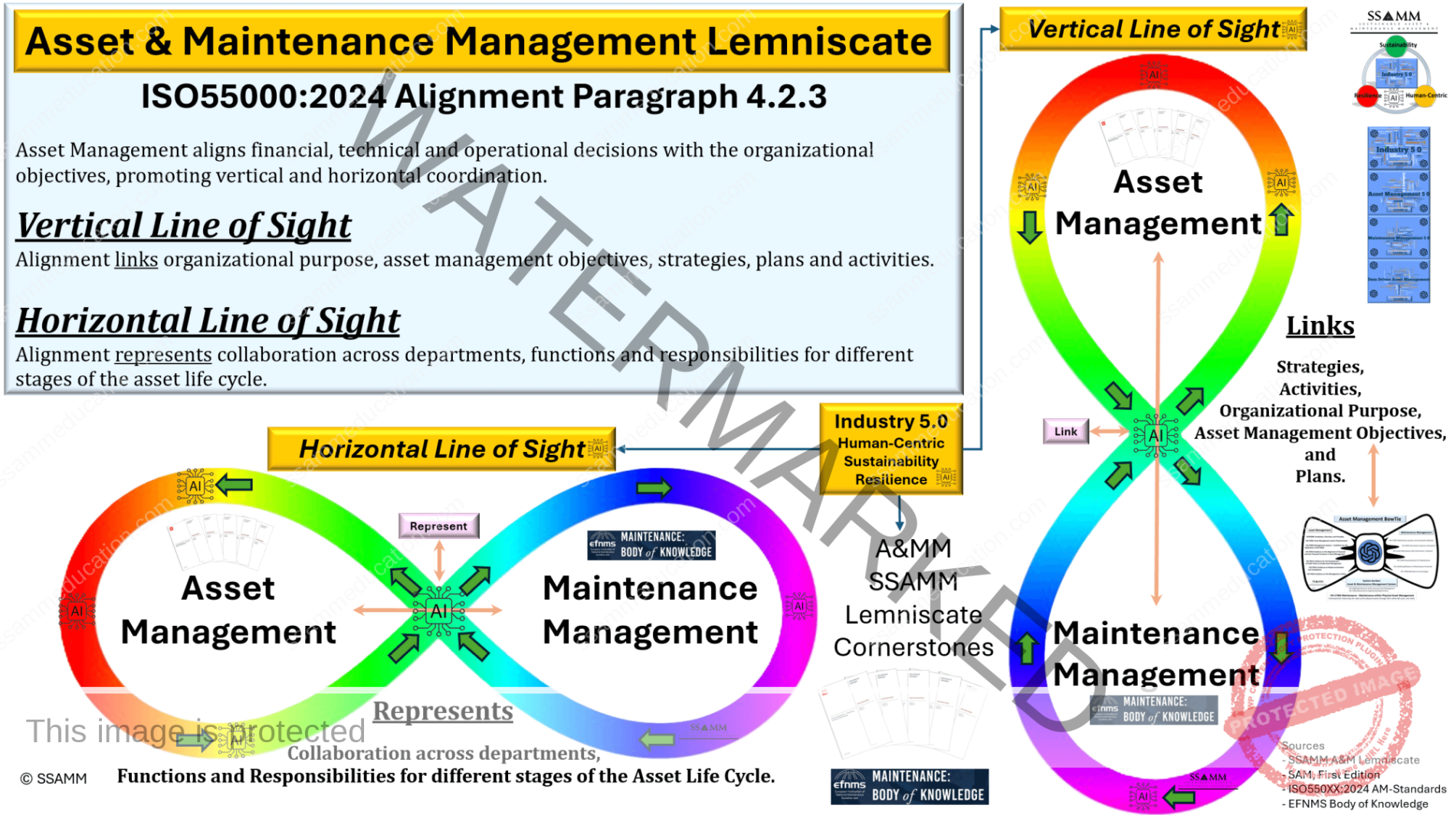
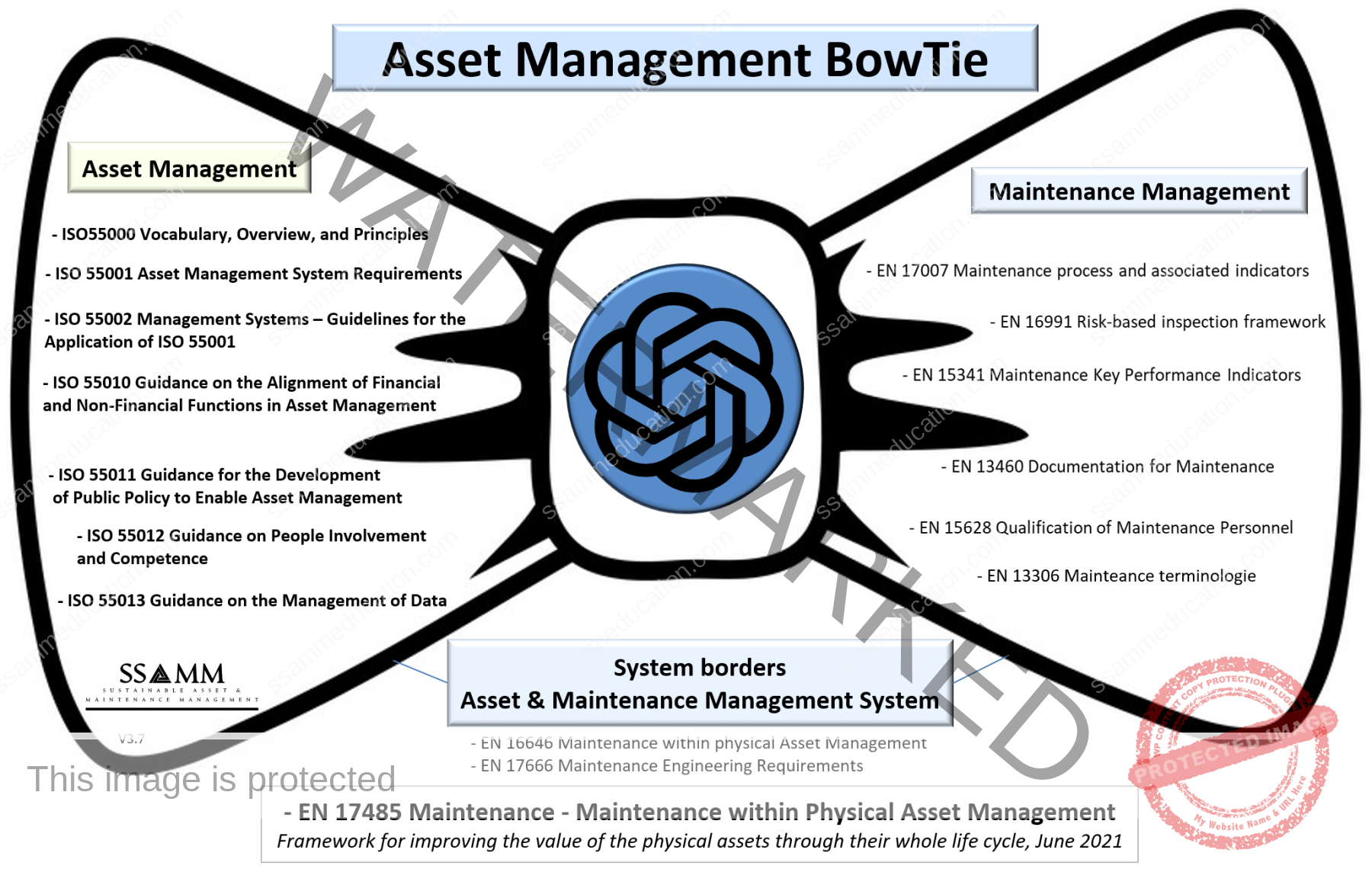
Key models such as the Asset Management Lemniscate and the Asset Management BowTie, alongside standards like EN 17007, EN 15628, EN 17485, and ISO 550XX:2024, provide the foundation for integrating maintenance engineering into broader asset management strategies. These frameworks emphasize the importance of structured maintenance processes, categorized into Management, Realization, and Support processes, which align maintenance tasks with organizational objectives, lifecycle planning, and risk mitigation.
This article explores the evolving role of maintenance engineering amidst Industry 5.0, focusing on its alignment with advanced standards and frameworks. By examining its processes, interactions, and impact on organizational resilience, we highlight how maintenance engineering transforms from a technical necessity into a cornerstone of sustainable and strategic asset management.
Maintenance Fundamentals SAM, First Edition Keynote Āpōpō Congres 2026 Follow Sustainable Asset Management for latest updates
Countdown SSAMM Academy Module 1
Explore the SSAMM Academy Asset Management and Maintenance Management courses.
Click Here for the Smart information page
Author: Ing. Jan Stoker MSc. MEng. AMCP. CFAM. Follow Jan Stoker
Introduction
Maintenance Engineering is a critical discipline within the broader field of Asset and Maintenance Management, ensuring that physical assets remain reliable, safe, and efficient throughout their lifecycle. In the context of Industry 5.0, this role takes on a new dimension, combining advanced technologies with human-centric approaches to create sustainable, resilient, and adaptive systems. Industry 5.0 moves beyond automation and digitalization, emphasizing collaboration between humans and intelligent systems while prioritizing sustainability and social responsibility.
Key frameworks such as the Asset Management Lemniscate and Asset Management BowTie, alongside standards like EN 17007, EN 15628, ISO 550XX:2024, and EN 17485, provide the structural foundation for integrating maintenance engineering into organizational strategies. These frameworks highlight the importance of aligning maintenance processes with asset management objectives, ensuring that maintenance actions are not isolated technical tasks but strategic enablers of long-term value creation. The structured categorization of maintenance processes into Management, Realization, and Support processes, as outlined in EN 17007, underscores the interdependence between strategy and operations.
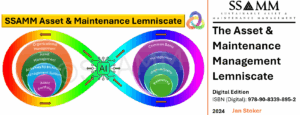
In the Industry 5.0 paradigm, maintenance engineering goes beyond ensuring asset functionality; it becomes a driver of sustainability and resilience. The Asset Management BowTie visualizes the dual roles of risk prevention and mitigation, enabling organizations to address vulnerabilities proactively while maintaining operational continuity. Similarly, the Asset Management Lemniscate emphasizes the continuous feedback loop between maintenance activities and strategic decision-making, ensuring that organizational strategies adapt to real-time operational data and lifecycle insights.
This article explores the evolving role of maintenance engineering within this transformative context. By integrating principles from established standards and frameworks, we examine how maintenance engineering contributes to sustainable asset management, risk mitigation, and organizational resilience. As Industry 5.0 reshapes the industrial landscape, maintenance engineering emerges as a cornerstone for achieving a balance between technological advancement and human-centric values, driving the future of sustainable and adaptive asset management.
1. Understanding Maintenance Engineering
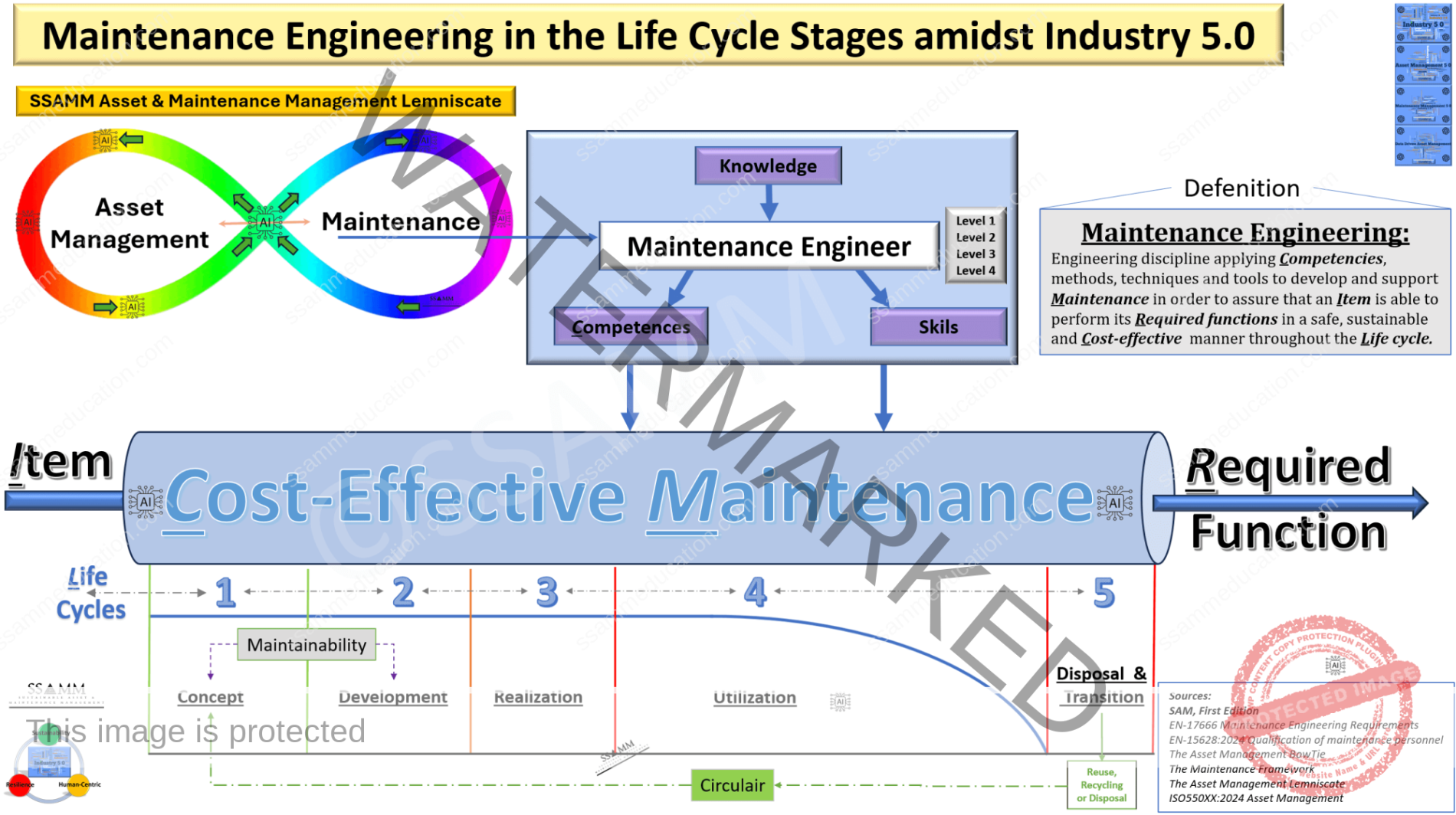
Maintenance engineering is a multidisciplinary field that plays a critical role in ensuring that physical assets perform their required functions throughout their lifecycle in a safe, sustainable, and cost-effective manner.
This chapter explores the scope, benefits, and foundational concepts of maintenance engineering, with a focus on its integration within the broader framework of Asset and Maintenance Management amidst the Industry 5.0 paradigm.
1.1 What is Maintenance Engineering….
Maintenance engineering is a specialized engineering discipline focused on applying competencies, methods, techniques, and tools to develop and support maintenance activities. Its primary goal is to ensure that assets or systems can reliably perform their required functions in a safe, sustainable, and cost-effective manner throughout their lifecycle.
By integrating technical expertise with strategic planning, maintenance engineering addresses operational reliability, risk management, and environmental considerations, positioning it as a cornerstone of effective asset management.
The defenition of Maintenance Engineering:
Maintenance Engineering
Engineering discipline applying Competencies, methods, techniques and tools to develop and support Maintenance in order to assure that an Item is able to perform its Required functions in a safe, sustainable and Cost-effective manner throughout the Life cycle
Sources:
- Body of Knowledge; EFNMS
- Maintainability; Blanchard, Verma & Peterson
- EN17666 Maintenance Engineering Requirements
1.2 Scope of Maintenance Engineering
Maintenance engineering is defined as the application of competencies, methods, techniques, and tools to develop and support maintenance. As outlined in standards such as EN 13306 and EN 17007, maintenance involves all technical, administrative, and managerial actions aimed at retaining or restoring an item to a state in which it can perform its required function. Maintenance engineering, therefore, provides the structured approach necessary to support these actions effectively.
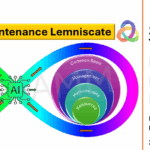
The scope of maintenance engineering extends across the entire lifecycle of an asset, encompassing design, operation, and disposal stages. Through activities like risk evaluation, task analysis, and failure management, maintenance engineering ensures assets remain dependable, environmentally sustainable, and aligned with stakeholder objectives. This lifecycle perspective ties directly into frameworks such as the Asset Management Lemniscate, which highlights the continuous feedback loop between asset strategy and operational activities.
1.3 Benefits of Maintenance Engineering
The benefits of maintenance engineering are broad and multifaceted, providing significant contributions to organizational success. One key benefit is the achievement of dependability goals by influencing design processes to incorporate maintainability and reliability considerations. This proactive approach reduces risks and ensures that assets perform optimally in various operational contexts.
Maintenance engineering also supports sustainability by reducing energy consumption and minimizing the environmental footprint of maintenance activities. By integrating principles from the Asset Management BowTie, it enhances safety and integrity, ensuring compliance with statutory and ethical requirements. Additionally, maintenance engineering contributes to life extension decisions, improved maintenance support, and optimized resource use, ultimately increasing the competitiveness and output value of organizations.
1.4 Core Concepts in Maintenance Engineering
The foundational concepts of maintenance engineering are rooted in a combination of technical, managerial, and analytical disciplines. Key components include:
-
Maintenance Plans: Structured and documented tasks that outline activities, procedures, resources, and timelines required for effective maintenance. These plans ensure that maintenance activities align with organizational goals and asset lifecycle needs.
-
Maintenance Strategies: Methods for achieving maintenance objectives, such as preventive, predictive, and corrective maintenance. These strategies are selected based on asset criticality, operational requirements, and risk assessments.
-
Failure Management Policies: Maintenance activities and design modifications aimed at mitigating the consequences of failures. By incorporating risk analysis tools, such as those outlined in EN 17666, organizations can prevent failures or minimize their impact.
-
Lifecycle Integration: Maintenance engineering ensures that actions are planned and executed with consideration for the asset’s entire lifecycle, linking design and operational phases to disposal strategies. This integration is central to the Asset Management Lemniscate, which reinforces the dynamic interaction between maintenance and asset strategy.
1.4 The Structured Approach to Maintenance Engineering
Maintenance engineering employs a structured methodology that combines scientific principles with practical tools to address maintenance challenges. This approach includes:
- Needs Analysis: Identifying objectives, timescales, and stakeholder requirements, such as safety, sustainability, and ethical considerations.
- Risk Evaluation: Assessing potential risks and determining mitigation strategies.
- Action Development: Creating and modeling maintenance actions, procedures, and proposals with an appropriate level of detail.
- Iteration and Implementation: Iteratively refining maintenance strategies based on operational feedback, followed by the implementation of agreed-upon decisions.
These steps align with global standards, including ISO 550XX:2024, which emphasize the strategic alignment of maintenance engineering with organizational objectives. The structured approach ensures that maintenance is not only effective in the short term but also contributes to the long-term reliability and sustainability of assets.
Click to enlarge
Wrap Up
Maintenance engineering serves as the backbone of modern asset management, ensuring that assets remain functional, efficient, and aligned with organizational goals. By integrating advanced methodologies and frameworks such as the Asset Management Lemniscate, Asset Management BowTie, and EN 17007, maintenance engineering transcends traditional reactive practices to become a strategic enabler of reliability, sustainability, and competitive advantage. This chapter has outlined the core scope, benefits, and principles of maintenance engineering, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of its application in the Industry 5.0 landscape.
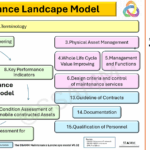
2. Maintenance Engineering life Stages amidst Industry 5.0
Maintenance engineering, as a cornerstone of Asset and Maintenance Management, plays a critical role in this context by ensuring that physical assets perform their required functions efficiently and sustainably across their lifecycle.
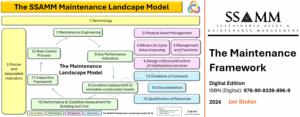
Central to maintenance engineering are the principles of maintainability and circularity, which align closely with the objectives of Industry 5.0. Maintainability focuses on designing and managing assets to be easily maintained, reducing downtime and resource consumption. Circularity extends this concept by emphasizing waste reduction through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, supporting the transition to a circular economy. These principles are reinforced by international standards such as EN 17666 and ISO 550XX:2024, and operationalized through frameworks like the Asset Management Lemniscate and the Maintenance Framework, which provide structured approaches to integrating maintenance engineering into broader asset strategies.
The integration of maintainability and circularity across all life cycle stages—concept, development, realization, utilization, and disposal/transition—ensures that assets contribute to long-term value creation while minimizing environmental impact. Maintenance engineers apply these principles through proactive planning, real-time monitoring, and iterative improvement processes. This approach aligns maintenance activities with organizational goals, regulatory requirements, and Industry 5.0’s emphasis on sustainability and resilience.
The evolution toward Maintenance 5.0, a concept rooted in the collaboration between human expertise and intelligent systems, further amplifies the role of maintenance engineering in achieving Industry 5.0 objectives. By leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), digital twins, and robotics, Maintenance 5.0 enables predictive and adaptive maintenance strategies that enhance asset performance while reducing costs and environmental impacts. This chapter explores the role of maintenance engineering within this transformative context, emphasizing its contribution to sustainable, efficient, and resilient industrial operations.
Click to enlarge
2.1 Concept Stage: Embedding Maintainability and Circularity in Design
The concept stage is the foundation of an asset’s lifecycle, where its purpose, functionality, and design principles are defined. At this stage, maintenance engineering plays a pivotal role in shaping the asset’s future performance by embedding maintainability and circularity into the design philosophy. These principles ensure that the asset can be efficiently maintained and that resource use aligns with sustainability goals. The decisions made during this stage establish the foundation for the asset’s operational efficiency, sustainability, and compliance with organizational and regulatory requirements throughout its lifecycle.
2.1.1 Maintainability in the Concept Stage
These standards define best practices for ensuring that maintenance actions, such as inspections, repairs, and component replacements, can be carried out with minimal effort, downtime, and resource consumption.
Using the Asset Management Lemniscate, maintenance engineers integrate lifecycle thinking into the design process, ensuring a feedback loop between strategic goals and operational needs. This approach enables the evaluation of design alternatives with a focus on factors such as accessibility, modularity, and the use of standardized components. For instance, ensuring that critical components are easily reachable for repair or replacement can significantly reduce downtime and labor costs, directly contributing to the asset’s dependability.
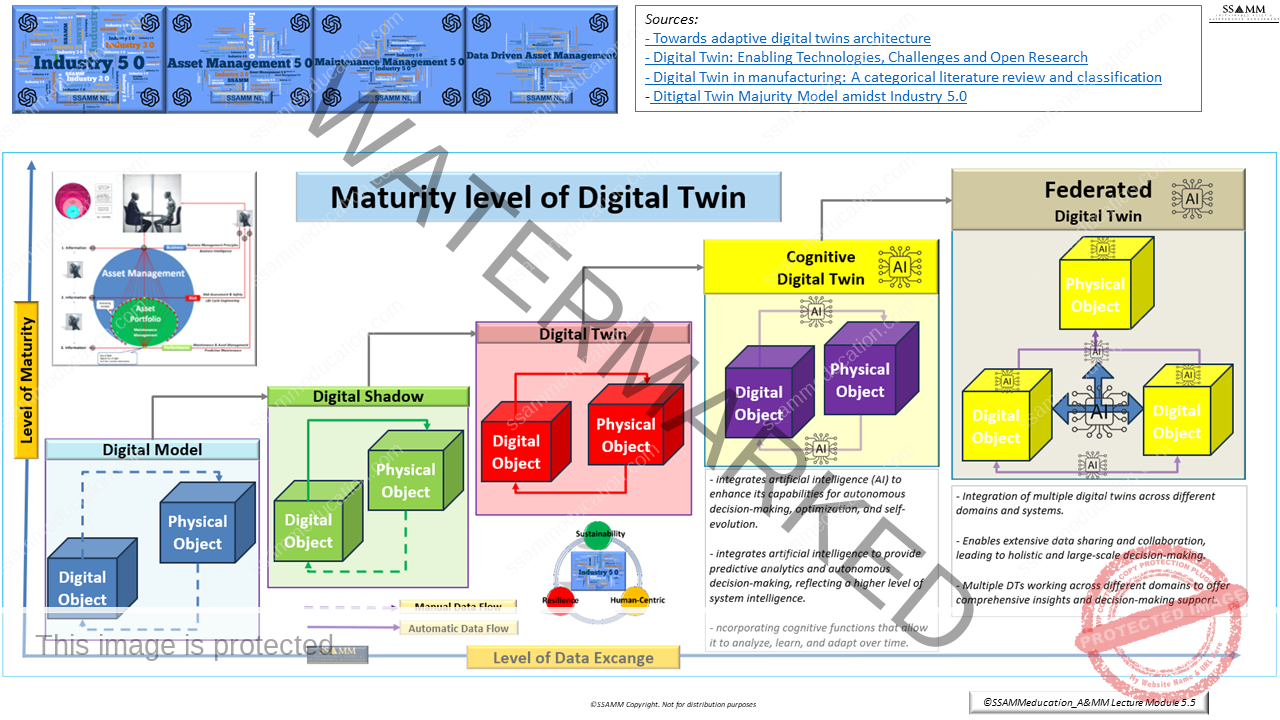
The use of advanced digital tools, such as digital twins, further enhances decision-making during this stage. Digital twins allow engineers to create virtual representations of the asset, enabling predictive simulations of maintenance scenarios. These simulations provide valuable insights into potential challenges, such as bottlenecks in maintenance workflows or the excessive wear of specific components. By identifying these issues early, engineers can refine design choices to optimize maintainability, ensuring alignment with the goals of the Maintenance Framework, which emphasizes efficient maintenance management as a strategic function.
2.1.2 Circularity in the Concept Stage
In addition to maintainability, circularity is a fundamental principle embedded in the concept stage, aligning with Industry 5.0’s emphasis on sustainability. Circularity focuses on designing assets with minimal environmental impact by enabling reuse, refurbishment, and recycling of materials and components. Maintenance engineers play a key role in guiding design decisions that reduce waste and extend the asset’s lifecycle, ensuring compliance with standards such as ISO 550XX:2024 and EN 17666.
Circular design strategies include selecting durable and recyclable materials, designing for disassembly, and incorporating components that can be refurbished or replaced rather than discarded. For example, modular designs not only simplify maintenance but also facilitate the replacement or upgrading of individual components, reducing the need for full-system replacements. These practices contribute to the circular economy, where resource efficiency and waste reduction are prioritized, aligning with global sustainability objectives.
By leveraging frameworks like the Asset Management BowTie, engineers visualize the risks and opportunities associated with circularity in design. The BowTie helps identify potential failure modes and their mitigation strategies, ensuring that design decisions consider both risk prevention and resource optimization. These insights are integral to creating assets that are not only functional but also environmentally sustainable throughout their lifecycle.
2.1.3 Anticipating Future Needs
A forward-looking perspective is crucial during the concept stage to ensure that assets remain adaptable to future operational and technological requirements. Maintenance engineers assess future-proofing considerations, such as the integration of emerging technologies like AI-driven predictive maintenance, IoT-enabled monitoring systems, and compatibility with evolving regulations. These assessments ensure that the asset’s design can accommodate future advancements and remain relevant in the dynamic landscape of Industry 5.0.
By using predictive modeling and scenario analysis, engineers can anticipate shifts in operational conditions, material availability, and energy consumption patterns. This proactive approach ensures that the asset’s design is resilient and adaptable, reducing the risk of obsolescence and supporting long-term value creation.
2.1.4 Aligning Design with Organizational Objectives
The decisions made during the concept stage must align with broader organizational objectives, including operational efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Maintenance engineers collaborate closely with stakeholders to ensure that design choices support these goals. This alignment is facilitated by the Asset Management Lemniscate, which ensures that maintenance considerations are integrated into strategic decision-making from the outset.
For example, an organization aiming to reduce its carbon footprint may prioritize designs that use energy-efficient materials and minimize waste.
Maintenance engineers contribute by evaluating these designs for maintainability, ensuring that sustainability goals do not compromise the asset’s functionality or reliability. This integrated approach ensures that the concept stage delivers a balance between operational needs and environmental responsibilities.
By embedding maintainability and circularity into the concept stage, maintenance engineering establishes the foundation for an asset’s efficient operation and sustainable lifecycle. Through collaboration, advanced tools, and adherence to standards, maintenance engineers ensure that early design decisions enable long-term value creation, aligning with both Industry 5.0 objectives and organizational goals. This proactive approach sets the stage for the subsequent lifecycle stages, where these foundational principles are further refined and realized.
2.2 Development Stage: Designing for Optimal Maintainability and Circularity
The development stage represents the transition from concept to detailed design, where initial ideas are refined into actionable plans and engineering blueprints. This stage is critical for embedding maintainability and circularity, as decisions made here directly influence the asset’s operational performance, lifecycle costs, and environmental impact. An iterative process, the development stage requires close collaboration between disciplines, integrating advanced tools and adhering to standards to ensure that maintainability and circularity objectives are met.
2.2.1 Preliminary Design
The preliminary design phase sets the groundwork for achieving optimal maintainability and circularity. Maintenance engineers actively participate in shaping design decisions by conducting maintainability analyses, focusing on critical factors such as reliability, accessibility, ease of repair, and downtime reduction. By adhering to standards such as EN 17666, engineers ensure that dependability and maintainability requirements are integrated into early design processes, laying the foundation for an asset that is both functional and sustainable.
Frameworks like the Asset Management Lemniscate are invaluable at this stage, enabling engineers to evaluate design alternatives through a lifecycle perspective. The Lemniscate emphasizes a feedback loop where operational insights and strategic goals influence design choices. Engineers use this approach to balance technical feasibility with environmental and economic considerations, ensuring that designs are robust yet adaptable to changing conditions.
The integration of digital tools, such as AI-driven analytics, digital twins, and simulation models, significantly enhances the preliminary design process. These technologies allow maintenance engineers to predict the long-term implications of design choices, identifying potential risks and optimizing solutions. For example, predictive simulations can reveal how specific design elements, such as component placement or material selection, impact maintenance efficiency over time. This proactive approach ensures that designs align with organizational sustainability goals and operational objectives while minimizing future maintenance burdens.
2.2.2 Detailed Design
The detailed design phase builds upon the preliminary work, translating conceptual ideas into precise engineering specifications, maintenance plans, and operational procedures. This phase is crucial for embedding both maintainability and circularity into the asset’s operational framework. Maintenance engineers develop structured maintenance plans, task descriptions, and repair procedures that ensure efficient and sustainable operations throughout the asset’s lifecycle.
Maintainability is further enhanced during detailed design by incorporating features that simplify maintenance activities. Examples include the integration of modular components that can be easily replaced or repaired, reducing downtime and maintenance effort. Modular designs also contribute to long-term cost savings by enabling individual component upgrades rather than full-system replacements. These considerations align with the guidance provided by the Maintenance Framework, which emphasizes a structured approach to developing maintenance strategies.
Circularity principles are emphasized through careful material selection, focusing on durability, recyclability, and environmental compatibility. Maintenance engineers work closely with material specialists to select resources that minimize environmental impact while ensuring long-term performance.
2.2.3 Iterative Collaboration
The development stage is inherently collaborative, involving input from diverse disciplines, including design, operations, sustainability, and risk management. Maintenance engineers act as a bridge between strategic goals and technical execution, ensuring that all stakeholders align with the overarching objectives of maintainability and circularity.
Frameworks such as the Asset Management BowTie support this collaboration by providing a clear visualization of risk pathways and mitigation strategies. The BowTie highlights how design decisions impact risk prevention and response, ensuring that all potential failure modes are addressed proactively. For instance, the integration of redundant systems to prevent critical failures or the selection of materials that can withstand extreme operational conditions are informed by insights derived from the BowTie model.
2.2.4 Strategic Alignment with Industry 5.0
The development stage reflects the broader principles of Industry 5.0, where sustainability and human-centricity are central to design and engineering practices. Maintenance engineers leverage advanced technologies and collaborative frameworks to ensure that the asset design aligns with these principles while achieving operational excellence.
By embedding maintainability and circularity into this stage, engineers enable organizations to meet their sustainability objectives, reduce lifecycle costs, and ensure long-term asset resilience.
Through iterative refinement, integration of advanced tools, and adherence to global standards, the development stage transforms the initial concept into a tangible, actionable framework for asset performance. This stage not only ensures that the asset is functional and efficient but also sets the foundation for achieving the long-term goals of sustainability and adaptability in the dynamic context of Industry 5.0.
2.3 Realization Stage: Implementing Maintenance and Circularity Strategies
The realization stage is a pivotal phase in the lifecycle of an asset, where conceptual designs are transformed into operational systems. This stage encompasses the construction, installation, and commissioning of the asset, ensuring that the principles of maintainability and circularity are effectively implemented. Maintenance engineers play a central role during this phase, overseeing the alignment of construction and commissioning activities with the planned maintenance strategies and sustainability objectives outlined during the earlier lifecycle stages.
By adhering to frameworks such as the Maintenance Framework and standards like EN 17666 and ISO 550XX:2024, the realization stage ensures that assets are built to facilitate efficient maintenance, minimize environmental impact, and achieve long-term value creation.
2.3.1 Build Phase
The build phase involves the physical construction and assembly of the asset, translating theoretical designs into tangible systems. Maintenance engineers oversee this process to ensure that the construction aligns with the maintainability objectives defined during the concept and development stages. A primary focus during this phase is verifying that components are installed in a way that supports easy access for inspection, repair, and replacement, critical to minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
To achieve these goals, engineers utilize the principles outlined in the Maintenance Framework, emphasizing the importance of traceability and compliance. Traceability ensures that the as-built conditions align with design specifications and maintenance strategies. For example, engineers verify that equipment layouts allow for unobstructed access to critical components and that modular designs are implemented to enable efficient replacements without requiring extensive disassembly.
Another critical aspect of the build phase is the incorporation of circularity principles. Maintenance engineers ensure that materials used during construction are selected for their durability, recyclability, and environmental impact. Waste minimization strategies, such as reusing surplus materials or implementing efficient supply chain logistics, are integral to reducing the environmental footprint of the construction process. These efforts align with Industry 5.0’s emphasis on sustainability, supporting organizations in achieving circular economy objectives.
2.3.2 Commissioning
The commissioning phase follows construction and focuses on preparing the asset for operational use. During this phase, maintenance engineers validate that the installed systems meet the required functional, safety, and performance standards. This involves rigorous testing, inspections, and simulations to ensure that the asset is fully operational and ready for sustained performance.
Validation of Maintenance Procedures:
A critical task during commissioning is the validation of maintenance procedures. Maintenance engineers ensure that the documented maintenance plans, task descriptions, and schedules are practical and effective under real-world conditions. This includes testing maintenance workflows to identify potential inefficiencies or bottlenecks, allowing for refinements before the asset enters full operation.
Integration of Circularity:
Circularity principles are further integrated during commissioning by identifying opportunities to reuse or repurpose materials leftover from construction. For example, unused components may be cataloged for future maintenance or refurbishment, while waste materials are recycled to minimize environmental impact. These actions reinforce the organization’s commitment to sustainability while reducing operational costs.
Training and Knowledge Transfer:
The commissioning phase also involves preparing personnel for ongoing maintenance tasks. Maintenance engineers use advanced tools, such as augmented reality (AR) and digital twins, to provide immersive training experiences. These technologies enable operators and maintenance teams to familiarize themselves with the asset’s systems and components, practicing maintenance tasks in a virtual environment. This approach not only enhances skill development but also reduces the risk of errors during actual operations.
2.3.3 Feedback and Optimization
The realization stage, particularly during commissioning, provides a valuable opportunity for feedback and optimization. Maintenance engineers use tools like the Asset Management Lemniscate to evaluate the outcomes of the commissioning process. The Lemniscate framework emphasizes the continuous feedback loop between strategy and operations, allowing engineers to assess how well the asset meets its design objectives and identify areas for improvement.
For example, data collected during initial operations can reveal unexpected wear patterns or inefficiencies in maintenance workflows. Engineers use this information to refine maintenance plans, update task descriptions, and recommend design modifications that enhance long-term performance. This iterative process ensures that the asset is optimized for operational efficiency, reliability, and sustainability before it enters full-scale use.
2.3.4 Aligning with Industry 5.0 Objectives
The realization stage exemplifies the principles of Industry 5.0, combining advanced technologies with human expertise to create sustainable and resilient assets.
By leveraging digital tools, adhering to global standards, and integrating frameworks like the Maintenance Framework and Asset Management BowTie, maintenance engineers ensure that assets are constructed and commissioned to meet the highest standards of maintainability and circularity. Through meticulous planning, execution, and validation, the realization stage bridges the gap between design and operation.
This stage not only brings the asset to life but also ensures that it is equipped to deliver long-term value while aligning with organizational goals and the broader sustainability and resilience objectives of Industry 5.0.
2.5 Disposal/Transition Stage: Facilitating Circular Economy Practices
The disposal or transition stage represents the final phase in an asset’s lifecycle, where decommissioning activities focus on responsible practices that align with circular economy principles. This stage is critical for ensuring that assets are removed, repurposed, or disposed of in a manner that minimizes environmental impact and maximizes resource efficiency. Maintenance engineers are central to this process, providing technical expertise and strategic oversight to ensure that the transition is carried out effectively, sustainably, and in compliance with organizational and regulatory requirements.
By leveraging frameworks such as the Asset Management Lemniscate and adhering to standards like EN-IEC 60760-2, maintenance engineers ensure that the disposal or transition stage contributes to long-term value creation, both economically and environmentally.
2.5.1 End-of-Life Assessments
At the heart of the disposal or transition stage are end-of-life assessments, where maintenance engineers evaluate the condition and remaining utility of assets and components. This involves identifying items that can be reused, refurbished, or recycled, thereby minimizing waste and supporting circular economy goals. Maintenance engineers assess the asset’s technical condition, historical performance data, and potential market value to determine the best course of action for each component.
The Asset Management Lemniscate plays a vital role in structuring these evaluations, as it emphasizes the feedback loop between operational insights and strategic decisions. Engineers use this framework to balance economic considerations, such as cost savings from component reuse, with environmental objectives, like reducing landfill contributions and conserving natural resources. For example, components with high residual value or limited wear can be refurbished for use in other systems, while materials like steel or copper can be recycled for future applications.
Advanced tools, including AI-powered analytics and digital twins, further enhance decision-making during end-of-life assessments. These tools analyze real-time and historical data to predict the remaining lifespan of components, identify potential risks associated with reuse, and recommend optimal disposal strategies.
By using these technologies, maintenance engineers can make data-driven decisions that align with both operational efficiency and sustainability objectives.
2.5.2 Circularity in Transition
The transition stage offers a unique opportunity to implement circularity principles, ensuring that materials and components are repurposed rather than discarded. Maintenance engineers collaborate with decommissioning teams to prioritize reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, aligning their actions with the sustainability goals outlined in standards such as EN-IEC 60760-2 and ISO 550XX:2024. For instance, high-value components like motors or control systems may be refurbished and reintegrated into other operations, reducing the demand for new resources.
Documentation and knowledge transfer are integral to ensuring the success of circularity initiatives. Maintenance engineers meticulously record the condition of decommissioned components, the processes used for their repurposing, and the lessons learned from the disposal stage. This information is invaluable for future projects, enabling organizations to refine their maintenance and disposal strategies over time. These activities align with the principles of Maintenance 5.0, which emphasizes the synergy between human expertise and intelligent systems in achieving sustainable outcomes.
Additionally, compliance with environmental regulations and organizational policies ensures that disposal practices align with broader goals of corporate responsibility. Maintenance engineers work closely with stakeholders to manage hazardous materials safely, optimize resource recovery, and minimize waste sent to landfills. This not only reduces the environmental impact of decommissioning activities but also enhances the organization’s reputation for sustainability and innovation.
2.5.3 Optimization Through Feedback Loops
The disposal or transition stage serves as a valuable source of feedback and continuous improvement, offering insights that inform future lifecycle planning and maintenance strategies. The Asset Management Lemniscate provides a structured framework for capturing and integrating these lessons into organizational practices, ensuring that experiences from decommissioned assets enhance the design and maintenance of future systems.
For example, recurring issues identified during decommissioning, such as component wear patterns or inefficiencies in material recycling, can guide the design of more robust and sustainable assets in subsequent projects. Similarly, data from this stage can refine failure management policies and maintenance schedules, reducing lifecycle costs and enhancing overall asset reliability.
Digital tools play a pivotal role in this feedback process. By analyzing decommissioning data through AI-driven platforms, maintenance engineers can identify trends, evaluate the effectiveness of circularity initiatives, and recommend design improvements that enhance maintainability and sustainability. This iterative approach ensures that the disposal or transition stage contributes to the continuous evolution of organizational strategies, aligning with Industry 5.0’s emphasis on resilience and adaptability.
2.5.4 Aligning with Industry 5.0 Objectives
The disposal or transition stage exemplifies the core principles of Industry 5.0, where human ingenuity and advanced technologies collaborate to create sustainable and socially responsible industrial systems. Maintenance engineers act as key facilitators of this vision, ensuring that end-of-life practices not only achieve operational efficiency but also contribute to broader environmental and economic goals.
By prioritizing circular economy practices, leveraging advanced tools, and adhering to global standards, the disposal or transition stage transforms the challenges of decommissioning into opportunities for value creation. This stage not only completes the lifecycle of an asset but also reinforces the organization’s commitment to sustainability, innovation, and long-term resilience in the ever-evolving industrial landscape.
3. Maintenance Engineering During the Utilization Stage
The utilization stage of the Maintenance Engineering Life Cycle encompasses the operational phase of an asset’s life. It is during this stage that maintenance engineering ensures assets meet their intended performance objectives, adapting strategies to real-world conditions and evolving organizational goals. This chapter delves into the primary activities, inputs, outputs, stakeholders, interfaces, and constraints relevant to maintenance engineering during the utilization stage, providing a detailed exploration of each component.
Click to enlarge
3.1 Primary Activities
Maintenance engineering during the utilization stage involves a broad range of interconnected activities, each designed to ensure the reliability, safety, and sustainability of assets. These activities span detailed analyses, task updates, root cause investigations, operator training, and resource planning.
3.1.1 System and Equipment Analyses
Maintenance engineers conduct detailed analyses of asset performance at both system and equipment levels. These analyses focus on metrics such as energy efficiency, lifecycle costs, and dependability. Engineers also assess compliance with health, safety, and environmental (HSE) standards to ensure operations align with regulatory requirements. Leveraging advanced tools such as IoT-enabled sensors and predictive analytics, engineers identify inefficiencies, emerging risks, and opportunities for optimization.
3.1.2 Task Analysis and Plan Updates
Regularly revisiting and updating maintenance plans is a core activity. Engineers perform task analyses to refine maintenance schedules, repair protocols, and condition-based maintenance strategies. Updates are informed by operational feedback, failure data, and the availability of resources. This ensures that maintenance practices remain relevant and effective in addressing both anticipated and unforeseen challenges.
3.1.3 Failure Management and Root Cause Analysis
Identifying and addressing the root causes of failures is critical for improving asset reliability. Maintenance engineers conduct thorough investigations into failure mechanisms, including factors such as wear, environmental conditions, and operational errors.
Insights gained from these analyses guide adjustments to maintenance plans, minimizing the recurrence of failures and enhancing overall system resilience.
3.1.4 Operator Skill Development
Collaboration between engineers and operators is essential for the successful implementation of maintenance strategies. Engineers provide training to improve operator skills, focusing on best practices for asset handling and maintenance execution. By equipping operators with the knowledge to identify early warning signs of failure, this collaboration reduces downtime and supports efficient operations.
3.1.5 Support Requirement Analyses
To ensure timely and effective maintenance interventions, engineers assess support requirements, including spare parts, tools, and skilled personnel. This proactive planning minimizes delays, reduces costs, and supports operational continuity. Advanced inventory management systems and digital tools are often employed to optimize resource allocation.
3.2 Input
The success of maintenance engineering during the utilization stage depends on a diverse range of inputs, which provide the data and context needed for effective decision-making and strategy development.
3.2.1 Operational Requirements
Inputs include detailed specifications for asset performance, availability, and reliability, as well as constraints related to budgets and timelines. These requirements serve as benchmarks against which maintenance strategies are evaluated and refined.
3.2.2 Asset and Maintenance History
Historical data on maintenance activities and asset performance provides valuable insights into patterns, trends, and areas requiring improvement. This includes information on previous failures, repair times, and the effectiveness of past maintenance actions.
3.2.3 Condition Monitoring and Failure Data
Real-time and historical condition monitoring data, collected through IoT sensors and diagnostic tools, allows engineers to assess asset health. Failure data, including failure modes, mechanisms, and detection methods, provides critical insights for root cause analysis and strategy optimization.
3.2.4 Resource and Regulatory Inputs
Inputs related to resource availability, including spare parts, tools, and skilled personnel, are essential for planning and executing maintenance activities. Additionally, compliance with regulatory and organizational policies influences maintenance priorities and practices.
3.3 Output
Maintenance engineering during the utilization stage produces a variety of outputs, each designed to enhance asset performance and contribute to long-term operational success.
3.3.1 Maintenance Performance Reports
Engineers generate comprehensive reports that detail asset performance, maintenance costs, and lifecycle evaluations. These reports verify assumptions made during earlier life cycle stages and provide data for refining maintenance strategies.
3.3.2 Recommendations for Improvement
Outputs include actionable recommendations for enhancing failure management policies, developing training programs, and refining support activities. These recommendations aim to optimize asset reliability, reduce costs, and align maintenance practices with organizational goals.
3.3.3 Plan Updates and Policy Modifications
Updated maintenance plans and failure management policies reflect changes in operational conditions, safety requirements, and asset performance. These modifications ensure that maintenance practices remain effective and adaptive.
3.3.4 Support for Modifications and Projects
Maintenance engineers provide technical expertise to support asset modifications and improvement projects. This ensures that these initiatives align with maintenance objectives and contribute to organizational success.
3.4 Stakeholders in Maintenance Engineering Output
Maintenance engineering outputs are vital to a diverse group of stakeholders, each of whom relies on these outputs to guide decision-making and strategy implementation.
3.4.1 Maintenance Management
Maintenance managers use engineering outputs to allocate resources, refine strategies, and oversee implementation. Detailed performance reports and recommendations provide the data needed to optimize maintenance activities and achieve organizational objectives.
3.4.2 Operations Teams
Operators rely on updated maintenance plans, training programs, and performance insights to guide daily practices. These outputs enable operators to maintain asset reliability while minimizing disruptions.
3.4.3 Safety and Environmental Teams
Safety and environmental stakeholders use maintenance engineering outputs to ensure compliance with HSE standards. Failure analyses and performance assessments help identify and mitigate potential risks.
3.4.4 Project Teams
Engineering outputs support project teams in planning and executing modifications and improvements. Technical recommendations ensure that these initiatives enhance asset performance and align with maintenance strategies.
3.5 Maintenance Engineering Interfaces
Effective maintenance engineering during the utilization stage requires seamless integration with other organizational functions. Key interfaces include:
3.5.1 Maintenance Management
Collaboration with maintenance managers ensures that engineering activities align with strategic goals and are supported by adequate resources. Regular communication facilitates the refinement of maintenance plans and strategies.
3.5.2 Safety and Environmental Management
Interfaces with safety and environmental teams ensure that maintenance activities address regulatory requirements and contribute to organizational compliance. This collaboration is particularly critical for high-risk operations.
3.5.3 Operations
Close coordination with operations teams ensures that maintenance activities are integrated into daily workflows, minimizing disruptions and maximizing asset availability.
3.5.4 Improvement Projects
Maintenance engineers work closely with project teams to provide technical expertise for modifications and upgrades. This ensures that improvement initiatives enhance asset performance and align with long-term maintenance objectives.
3.6 Constraints
Despite its critical importance, maintenance engineering during the utilization stage faces several challenges that can impact its effectiveness.
3.6.1 Data Quality Issues
Incomplete or inconsistent maintenance data can hinder analysis and decision-making. Addressing this constraint requires robust data management systems and disciplined reporting practices.
3.6.2 Resource Limitations
Constraints on personnel, tools, spare parts, or budgetary allocations can delay maintenance activities and reduce asset performance. Proactive resource planning and optimization are essential to mitigate these challenges.
3.6.3 Technological Gaps
The absence of advanced tools, such as predictive analytics and IoT-enabled sensors, can limit the ability of engineers to monitor asset performance and respond effectively to emerging issues. Investments in technology and training are necessary to bridge this gap.
3.9.4 Integration Challenges
Poor coordination between maintenance engineering and other organizational functions can result in misaligned strategies and inefficiencies. Clear communication channels and well-defined interfaces are critical for overcoming this constraint.
Maintenance engineering during the utilization stage is a dynamic and multifaceted discipline that balances immediate operational demands with long-term strategic goals. By focusing on core activities, leveraging comprehensive inputs, producing actionable outputs, and collaborating with stakeholders, maintenance engineering ensures that assets perform reliably, sustainably, and cost-effectively. Addressing constraints and fostering effective interfaces further enhances its impact, positioning maintenance engineering as a cornerstone of organizational success and resilience.