In his ‘Learning Journey’ of defining Asset & Maintenance Management, lecturer/Researcher Jan Stoker of SSAMM write his finding and insights during this journey. Started in 2013 with his research, one of his goals is to understand Asset & Maintenance Management within the ISO55000 framework. Currently, his main goal is to describe and define Asset Management 5.0 based on this article. Check the related article’s on this page.
Publication 8 October 2023
- Industry 5.0: Deepening The Subject
- The Asset & Maintenance Management Pyramid
- The Digital Line of Sight: Deepening the subject
- Maintenance Management: Deepening the subject
- Digital Twin: Deepening the subject
- The Asset Management BowTie
- Conference Article
- Article IR5.0 Human-Centric
- The IR5.0 elephant in the room
- Decision-making with AI
- AM 5.0: Balancing Risk, Performance and Value
With the rise of new technologies and methods, maintenance strategies have become more efficient, resulting in improved asset performance and cost savings. In this document, we will explore how the industrial revolution has shaped modern-day. Asset & Maintenance Management and its implications for the future. So let’s dive into the world of maintenance concepts that have emerged during this revolutionary period. By understanding the impact of industrial revolution on Asset & Maintenance Management, we can better prepare ourselves for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. So let’s explore the past, present, and future of maintenance management in light of industrial revolutions. Maintenance Fundamentals SAM, First Edition Keynote Āpōpō Congres 2026 Follow Sustainable Asset Management for latest updates
Author: Ing. Jan Stoker MSc. MEng. AMCP. CFAM. Follow Jan Stoker
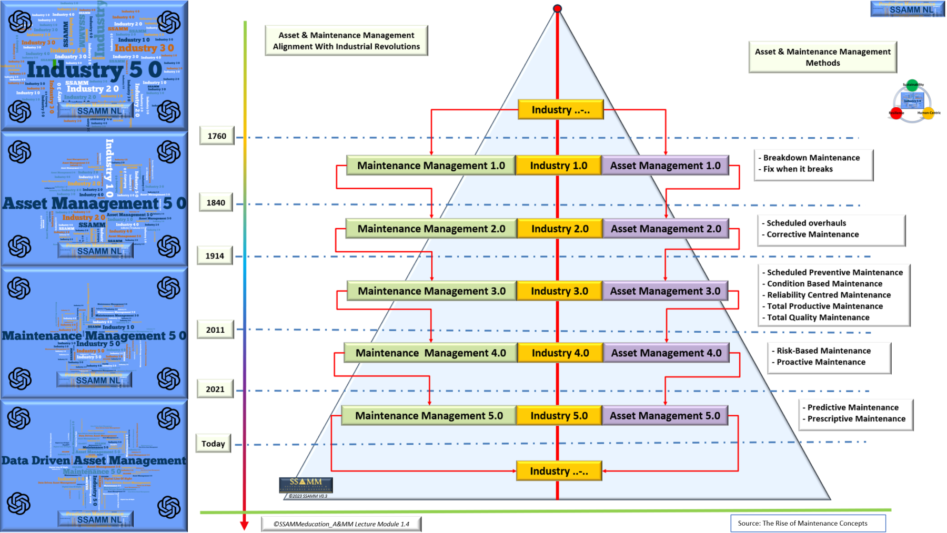
The Industrial Revolution had a profound effect on the field of maintenance and reliability. During this time period, techniques, processes, tools, and machinery used to create products were constantly advancing in complexity. As such, maintenance concepts or strategies and methods changed drastically as well – becoming more specialized than ever before.
In this a maintenance concept or strategy is defined according to the EN13306:2019 version:
A maintenance concept/strategy, as defined by the EN13306:2019 standard, is a structured approach to asset management that aims to maximize asset performance while minimizing costs and risks. It involves planning and implementing strategies for the inspection, repair, replacement, and improvement of assets throughout their life cycle.
The concept of maintenance has evolved significantly over time, especially with the advent of industrial revolutions. With each new revolution, there have been advancements in technology and methodologies, leading to the emergence of new maintenance concepts and strategies that aim to optimize asset performance and minimize costs.
For instance, during the first industrial revolution, which focused on mechanization, maintenance was primarily reactive and based on repairing equipment only when it broke down. As machinery became more complex and expensive, this approach proved to be inefficient and costly.
With the second industrial revolution, which was marked by mass production and assembly lines, preventative maintenance strategies were introduced. This involved regular inspections and maintenance activities to prevent breakdowns and improve asset reliability.
The third industrial revolution, also known as the digital revolution, brought about the concept of predictive maintenance. With advancements in technology and data analysis, it became possible to predict when an asset would fail and plan maintenance activities accordingly.
The fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, maintenance concepts are becoming even more advanced with the use of smart sensors, artificial intelligence, and real-time data. This has led to the emergence of proactive maintenance strategies, where assets are continuously monitored and maintenance activities are performed before any signs of failure occur.
Now in the fifth Industrial Revolution (Industry 5.o) A.I. will underpin maintenance concepts and bring quality and level up the outcome of the well-known maintenance strategies that already exist.
As we move into the fifth industrial revolution, maintenance concepts are set to become even more advanced with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). AI will play a crucial role in asset management, providing real-time insights and predictions to optimize performance and minimize costs. One major benefit of AI in maintenance is its ability to analyse large amounts of data from various sources, including sensors, historical maintenance records, and even weather patterns. This allows for more accurate predictions and proactive maintenance strategies.
Another advantage of AI is its ability to learn and adapt over time. As it collects data and identifies patterns, it can continuously improve its predictions and make more precise recommendations for maintenance activities. In addition to optimizing asset performance, AI in maintenance can also improve safety by identifying potential hazards and predicting failures before they occur. This allows for preventive maintenance to be performed, reducing the risk of accidents and downtime.
Moreover, with the use of AI, maintenance activities can be automated and performed remotely, reducing the need for human intervention and increasing efficiency. This not only saves time and resources but also allows for employees to focus on more critical tasks. However, the integration of AI in maintenance strategies does not mean that human expertise and experience will become obsolete. In fact, it is essential to have a combination of both AI and human knowledge to achieve the best results. While AI can analyse data and make predictions, it still requires human supervision and decision-making.
The fifth industrial revolution will bring significant advancements in maintenance concepts with the integration of AI. By utilizing its capabilities, industries can achieve better asset performance, cost savings, and improved safety. It is essential to embrace this technology and continue to develop it in collaboration with human expertise for a more efficient and sustainable future. Let us work together to unlock the full potential of AI in maintenance and create a better world for generations to come. We must also ensure that ethical considerations are taken into account and AI is used responsibly, to avoid any negative consequences. Let us embrace the possibilities of AI in maintenance and pave the way for a more innovative and prosperous future.
1. Maintenance concepts
For this text are used the most well-know maintenance concepts like:
- Break-down maintenance
- Corrective Maintenance
- Scheduled preventive Maintenance
- Condition Based Maintenance
- Reliability Centred Maintenance
- Total Productive Maintenance
- Risk-Based Maintenance
- Proactive Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance
- Prescriptive Maintenance
These concepts have been used for decades in industries to maintain their assets and ensure smooth operations. However, with the integration of AI, these traditional approaches are being revolutionized. Important is the to underline the différance between a maintenance concept/strategy and the methods to create a strategy.